Page 147 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 147
Coupled Supercritical Fluid and Chromatographic Techniques 139
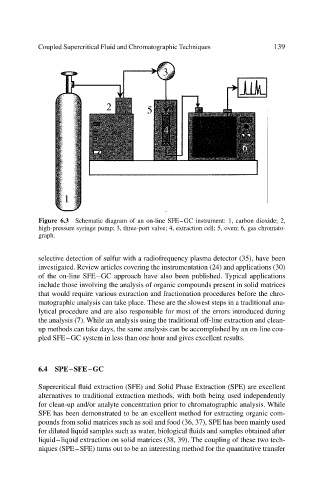
Figure 6.3 Schematic diagram of an on-line SFE–GC instrument: 1, carbon dioxide; 2,
high-pressure syringe pump; 3, three-port valve; 4, extraction cell; 5, oven; 6, gas chromato-
graph.
selective detection of sulfur with a radiofrequency plasma detector (35), have been
investigated. Review articles covering the instrumentation (24) and applications (30)
of the on-line SFE–GC approach have also been published. Typical applications
include those involving the analysis of organic compounds present in solid matrices
that would require various extraction and fractionation procedures before the chro-
matographic analysis can take place. These are the slowest steps in a traditional ana-
lytical procedure and are also responsible for most of the errors introduced during
the analysis (7). While an analysis using the traditional off-line extraction and clean-
up methods can take days, the same analysis can be accomplished by an on-line cou-
pled SFE–GC system in less than one hour and gives excellent results.
6.4 SPE–SFE–GC
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) and Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) are excellent
alternatives to traditional extraction methods, with both being used independently
for clean-up and/or analyte concentration prior to chromatographic analysis. While
SFE has been demonstrated to be an excellent method for extracting organic com-
pounds from solid matrices such as soil and food (36, 37), SPE has been mainly used
for diluted liquid samples such as water, biological fluids and samples obtained after
liquid–liquid extraction on solid matrices (38, 39). The coupling of these two tech-
niques (SPE–SFE) turns out to be an interesting method for the quantitative transfer