Page 288 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 288
Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications 283
(a) (b) (c)
C L
L
C
L
C
M ?
M M ?
0 5 10 0 5 10 0 5 10
Retention time (min)
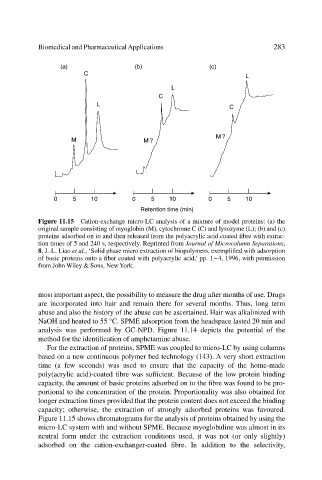
Figure 11.15 Cation-exchange micro-LC analysis of a mixture of model proteins: (a) the
original sample consisting of myoglobin (M), cytochrome C (C) and lysozyme (L); (b) and (c)
proteins adsorbed on to and then released from the polyacrylic acid coated fibre with extrac-
tion times of 5 and 240 s, respectively. Reprinted from Journal of Microcolumn Separations,
8, J.-L. Liao et al., ‘Solid phase micro extraction of biopolymers, exemplified with adsorption
of basic proteins onto a fiber coated with polyacrylic acid,’ pp. 1–4, 1996, with permission
from John Wiley & Sons, New York.
most important aspect, the possibility to measure the drug after months of use. Drugs
are incorporated into hair and remain there for several months. Thus, long term
abuse and also the history of the abuse can be ascertained. Hair was alkalinized with
NaOH and heated to 55 °C. SPME adsorption from the headspace lasted 20 min and
analysis was performed by GC-NPD. Figure 11.14 depicts the potential of the
method for the identification of amphetamine abuse.
For the extraction of proteins, SPME was coupled to micro-LC by using columns
based on a new continuous polymer bed technology (143). A very short extraction
time (a few seconds) was used to ensure that the capacity of the home-made
poly(acrylic acid)-coated fibre was sufficient. Because of the low protein binding
capacity, the amount of basic proteins adsorbed on to the fibre was found to be pro-
portional to the concentration of the protein. Proportionality was also obtained for
longer extraction times provided that the protein content does not exceed the binding
capacity; otherwise, the extraction of strongly adsorbed proteins was favoured.
Figure 11.15 shows chromatograms for the analysis of proteins obtained by using the
micro-LC system with and without SPME. Because myoglobuline was almost in its
neutral form under the extraction conditions used, it was not (or only slightly)
adsorbed on the cation-exchanger-coated fibre. In addition to the selectivity,