Page 33 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 33
Coupled HPLC with HRGC 23
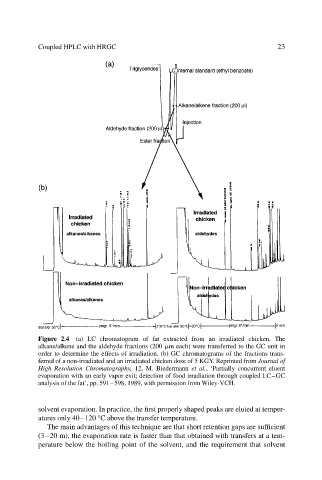
Figure 2.4 (a) LC chromatogram of fat extracted from an irradiated chicken. The
alkane/alkene and the aldehyde fractions (200 m each) were transferred to the GC unit in
order to determine the effects of irradiation. (b) GC chromatograms of the fractions trans-
ferred of a non-irradiated and an irradiated chicken dose of 5 KGY. Reprinted from Journal of
High Resolution Chromatography, 12, M. Biedermann et al., ‘Partially concurrent eluent
evaporation with an early vapor exit; detection of food irradiation through coupled LC–GC
analysis of the fat’, pp. 591–598, 1989, with permission from Wiley-VCH.
solvent evaporation. In practice, the first properly shaped peaks are eluted at temper-
atures only 40–120 °C above the transfer temperature.
The main advantages of this technique are that short retention gaps are sufficient
(3–20 m), the evaporation rate is faster than that obtained with transfers at a tem-
perature below the boiling point of the solvent, and the requirement that solvent