Page 34 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 34
24 Multidimensional Chromatography
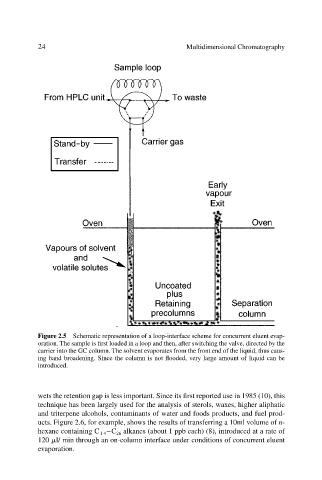
Figure 2.5 Schematic representation of a loop-interface scheme for concurrent eluent evap-
oration. The sample is first loaded in a loop and then, after switching the valve, directed by the
carrier into the GC column. The solvent evaporates from the front end of the liquid, thus caus-
ing band broadening. Since the column is not flooded, very large amount of liquid can be
introduced.
wets the retention gap is less important. Since its first reported use in 1985 (10), this
technique has been largely used for the analysis of sterols, waxes, higher aliphatic
and triterpene alcohols, contaminants of water and foods products, and fuel prod-
ucts. Figure 2.6, for example, shows the results of transferring a 10ml volume of n-
hexane containing C 14 –C 26 alkanes (about 1 ppb each) (8), introduced at a rate of
120 l/ min through an on-column interface under conditions of concurrent eluent
evaporation.