Page 44 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 44
34 Multidimensional Chromatography
a recent paper (33), three drying agents and four solvents were tested by using a mix-
ture of 24 microcontaminants ranging widely in polarity and volatility. Silica was
preferred among the drying agents investigated (sodium sulfate, silica and molecular
sieves), while methyl acetate was the preferred solvent after examining pentane, hex-
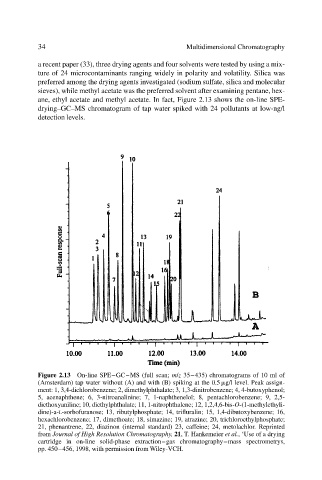
ane, ethyl acetate and methyl acetate. In fact, Figure 2.13 shows the on-line SPE-
drying–GC–MS chromatogram of tap water spiked with 24 pollutants at low-ng/l
detection levels.
Figure 2.13 On-line SPE–GC–MS (full scan; m/z 35–435) chromatograms of 10 ml of
(Amsterdam) tap water without (A) and with (B) spiking at the 0.5 g/l level. Peak assign-
ment: 1, 3,4-dichlorobenzene; 2, dimethylphthalate; 3, 1,3-dinitrobenzene; 4, 4-butoxyphenol;
5, acenaphthene; 6, 3-nitroanalinine; 7, 1-naphthenelol; 8, pentachlorobenzene; 9, 2,5-
diethoxyaniline; 10, diethylphthalate; 11, 1-nitrophthalene; 12, 1,2,4,6-bis-O-(1-methylethyli-
dine)-a-L-sorbofuranose; 13, ributylphosphate; 14, trifluralin; 15, 1,4-dibutoxybenzene; 16,
hexachlorobenzene; 17, dimethoate; 18, simazine; 19, atrazine; 20, trichloroethylphosphate;
21, phenantrene, 22, diazinon (internal standard) 23, caffeine; 24, metolachlor. Reprinted
from Journal of High Resolution Chromatography, 21, T. Hankemeier et al., ‘Use of a drying
cartridge in on-line solid-phase extraction–gas chromatography–mass spectrometrys,
pp. 450–456, 1998, with permission from Wiley-VCH.