Page 117 - Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
P. 117
106 Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
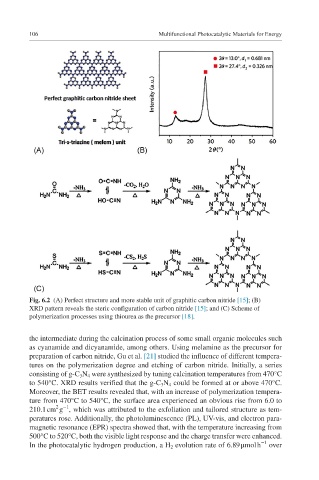
Fig. 6.2 (A) Perfect structure and more stable unit of graphitic carbon nitride [15]; (B)
XRD pattern reveals the steric configuration of carbon nitride [15]; and (C) Scheme of
polymerization processes using thiourea as the precursor [18].
the intermediate during the calcination process of some small organic molecules such
as cyanamide and dicyanamide, among others. Using melamine as the precursor for
preparation of carbon nitride, Gu et al. [21] studied the influence of different tempera-
tures on the polymerization degree and etching of carbon nitride. Initially, a series
consisting of g-C 3 N 4 were synthesized by tuning calcination temperatures from 470°C
to 540°C. XRD results verified that the g-C 3 N 4 could be formed at or above 470°C.
Moreover, the BET results revealed that, with an increase of polymerization tempera-
ture from 470°C to 540°C, the surface area experienced an obvious rise from 6.0 to
2 −1
210.1 cm g , which was attributed to the exfoliation and tailored structure as tem-
peratures rose. Additionally, the photoluminescence (PL), UV-vis, and electron para-
magnetic resonance (EPR) spectra showed that, with the temperature increasing from
500°C to 520°C, both the visible light response and the charge transfer were enhanced.
−1
In the photocatalytic hydrogen production, a H 2 evolution rate of 6.89 μmol h over