Page 129 - Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
P. 129
Carbon nitride photocatalysts 115
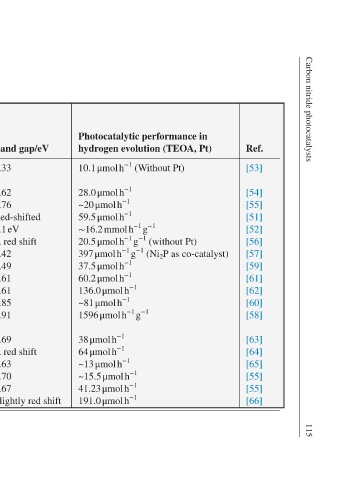
Ref. [53] [54] [55] [51] [52] [56] [57] [59] [61] [62] [60] [58] [63] [64] [65] [55] [55] [66]
Photocatalytic performance in hydrogen evolution (TEOA, Pt) 10.1 μmol h −1 (Without Pt) 28.0 μmol h −1 ~20 μmol h −1 59.5 μmol h −1 ∼16.2 mmol h −1 g −1 20.5 μmol h −1 g −1 (without Pt) 397 μmol h −1 g −1 (Ni 2 P as co-catalyst) 37.5 μmol h −1 60.2 μmol h −1 136.0 μmol h −1 ~81 μmol h −1 1596 μmol h
Band gap/eV 2.33 2.62 2.76 Red-shifted 1.1 eV A red shift 2.42 2.49 2.61 2.61 2.85 2.91 2.69 A red shift 2.63 2.70 2.67 Slightly red shift
Polymerization parameters (annealing temp, duration, and atmosphere) Photoreduction, subsequently calcination 300°C, 1 h, air 550°C, 4 h 550°C, 4 h, air 400°C, 4 h, N 2 Hydrothermal treatment 45°C, 3 h, H 2 (5 vol%) and Ar 400°C, 2 h, Ar Hydrothermal treatment 550°C, 2 h, N 2 Hard template method 450°C, 1
Doped carbon nitride and its properties
Cobalt phthalocyanine Ferric nitrate nonahydrate 2-Aminoethylphosphonic Ammonium iodine Citric acid monohydrate Potassium iodine Sodium tripolyphosphate
Dopant AgNO 3 KNO 3 ZnCl 2 FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O Cu(NO 3 ) 2 H 2 O 2 H 2 O 2 Thiourea H 2 S acid NH 4 F NH 4 I
Table 6.2 Doped element Ag Co K Zn Fe Cu Fe O O S S P I N F I K, I Na, P