Page 148 - Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
P. 148
134 Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
materials in DSSCs, OVCs, PSCs, and heterojunction solar cells. It also sheds light
on various advancements in the material development processes employed to achieve
enhanced device performances.
7.4 Graphene in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs)
In 1991 Micheal Graztel reported on mesoporous TiO 2 nanoparticle-based DSSCs with
an efficiency of 7.1%, which opened the door to alternatives to p-n convection solar cells
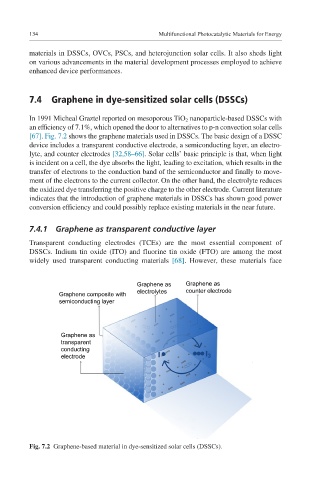
[67]. Fig. 7.2 shows the graphene materials used in DSSCs. The basic design of a DSSC
device includes a transparent conductive electrode, a semiconducting layer, an electro-
lyte, and counter electrodes [32,58–66]. Solar cells’ basic principle is that, when light
is incident on a cell, the dye absorbs the light, leading to excitation, which results in the
transfer of electrons to the conduction band of the semiconductor and finally to move-
ment of the electrons to the current collector. On the other hand, the electrolyte reduces
the oxidized dye transferring the positive charge to the other electrode. Current literature
indicates that the introduction of graphene materials in DSSCs has shown good power
conversion efficiency and could possibly replace existing materials in the near future.
7.4.1 Graphene as transparent conductive layer
Transparent conducting electrodes (TCEs) are the most essential component of
DSSCs. Indium tin oxide (ITO) and fluorine tin oxide (FTO) are among the most
widely used transparent conducting materials [68]. However, these materials face
Graphene as Graphene as
Graphene composite with electrolytes counter electrode
semiconducting layer
Graphene as
transparent
conducting
electrode I I 3
Fig. 7.2 Graphene-based material in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs).