Page 19 - Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
P. 19
8 Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
The photoactivation of a metal oxide photocatalyst is based on its electronic exci-
tation by photons (light) with energy (hv) greater than the band gap energy (E g ). The
electrons migrate after the excitation, generating vacancies in the VB (holes, h+) and
−
forming regions with high electron density (e ) in the CB [15,17–22]. These holes have
pH-dependent and strongly positive electrochemical potentials, ranging between +2.0
and +3.5 V, measured against a saturated calomel electrode [20]. This potential is suf-
•
ficiently positive to generate hydroxyl radicals ( OH) from water molecules adsorbed
on the surface of the metal oxides (Eqs. 2.1–2.3). The photocatalytic efficiency de-
−
+
pends on the competition between the formation of e /h pairs and the recombination
of these pairs (Eq. 2.4) on the metal oxide surfaces [17,21,22].
+
+
Metal oxide hv ® Metal oxide e ( - CB + h ) (2.1)
VB
+
·
h + HO . ® HO + H + (2.2)
2 ads
h + OH - . ® HO (2.3)
+
ads
Metal oxide e ( - CB + h ) ® Metal oxide + D (2.4)
+
VB
Although the oxidation reactions caused by the generated holes occur at the VB, the
electrons transferred to the CB are responsible for reduction reactions, such as the for-
mation of gaseous hydrogen and the generation of other important oxidizing species
such as superoxide anion radicals. In the case of metal oxides, the E g is between 3.00
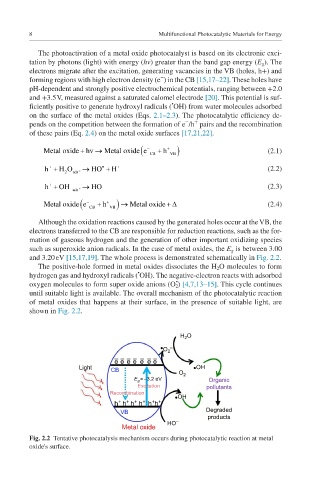
and 3.20 eV [15,17,19]. The whole process is demonstrated schematically in Fig. 2.2.
The positive-hole formed in metal oxides dissociates the H 2 O molecules to form
•
hydrogen gas and hydroxyl radicals ( OH). The negative-electron reacts with adsorbed
•
oxygen molecules to form super oxide anions (O 2 ) [4,7,13–15]. This cycle continues
until suitable light is available. The overall mechanism of the photocatalytic reaction
of metal oxides that happens at their surface, in the presence of suitable light, are
shown in Fig. 2.2.
H O
2
•
–
O
2
– – – – – – –
e e e e e e e
Light CB •OH
O 2
E = ∼3.2 eV Organic
g
Excitation pollutants
Recombination •OH
+ + +
+
+ +
h h h h h h
VB Degraded
products
HO –
Metal oxide
Fig. 2.2 Tentative photocatalysis mechanism occurs during photocatalytic reaction at metal
oxide's surface.