Page 98 - Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
P. 98
Graphene photocatalysts 87
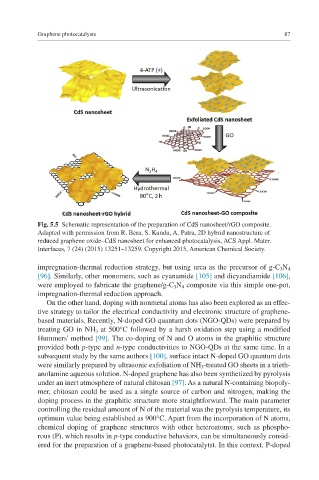
Fig. 5.5 Schematic representation of the preparation of CdS nanosheet/rGO composite.
Adapted with permission from R. Bera, S. Kundu, A. Patra, 2D hybrid nanostructure of
reduced graphene oxide–CdS nanosheet for enhanced photocatalysis, ACS Appl. Mater.
Interfaces, 7 (24) (2015) 13251–13259. Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society.
impregnation-thermal reduction strategy, but using urea as the precursor of g-C 3 N 4
[96]. Similarly, other monomers, such as cyanamide [105] and dicyandiamide [106],
were employed to fabricate the graphene/g-C 3 N 4 composite via this simple one-pot,
impregnation-thermal reduction approach.
On the other hand, doping with nonmetal atoms has also been explored as an effec-
tive strategy to tailor the electrical conductivity and electronic structure of graphene-
based materials. Recently, N-doped GO quantum dots (NGO-QDs) were prepared by
treating GO in NH 3 at 500°C followed by a harsh oxidation step using a modified
Hummers' method [99]. The co-doping of N and O atoms in the graphitic structure
provided both p-type and n-type conductivities to NGO-QDs at the same time. In a
subsequent study by the same authors [100], surface intact N-doped GO quantum dots
were similarly prepared by ultrasonic exfoliation of NH 3 -treated GO sheets in a trieth-
anolamine aqueous solution. N-doped graphene has also been synthetized by pyrolysis
under an inert atmosphere of natural chitosan [97]. As a natural N-containing biopoly-
mer, chitosan could be used as a single source of carbon and nitrogen, making the
doping process in the graphitic structure more straightforward. The main parameter
controlling the residual amount of N of the material was the pyrolysis temperature, its
optimum value being established as 900°C. Apart from the incorporation of N atoms,
chemical doping of graphene structures with other heteroatoms, such as phospho-
rous (P), which results in p-type conductive behaviors, can be simultaneously consid-
ered for the preparation of a graphene-based photocatalytst. In this context, P-doped