Page 238 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 238
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 4 CONTROL OF NANOSTRUCTURE OF MATERIALS
Intercalation with
organic cation
+
+ + +
+ + + +
+
Monomer mixing/
polymerization
+
+
+
+
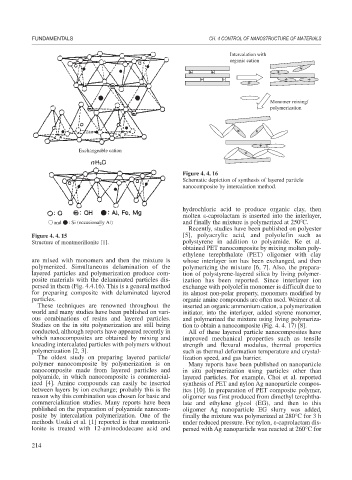
Figure 4. 4. 16
Schematic depiction of synthesis of layered particle
nanocomposite by intercalation method.
hydrochloric acid to produce organic clay, then
molten
-caprolactam is inserted into the interlayer,
and finally the mixture is polymerized at 250 C.
Recently, studies have been published on polyester
Figure 4. 4. 15 [5], polyacrylic acid, and polyolefin such as
Structure of montmorillonite [1]. polystyrene in addition to polyamide. Ke et al.
obtained PET nanocomposite by mixing molten poly-
ethylene terephthalate (PET) oligomer with clay
are mixed with monomers and then the mixture is whose interlayer ion has been exchanged, and then
polymerized. Simultaneous delamination of the polymerizing the mixture [6, 7]. Also, the prepara-
layered particles and polymerization produce com- tion of polystyrene-layered silica by living polymer-
posite materials with the delaminated particles dis- ization has been reported. Since interlayer ion
persed in them (Fig. 4.4.16). This is a general method exchange with polyolefin monomer is difficult due to
for preparing composite with delaminated layered its almost non-polar property, monomers modified by
particles. organic amine compounds are often used. Weimer et al.
These techniques are renowned throughout the inserted an organic ammonium cation, a polymerization
world and many studies have been published on vari- initiator, into the interlayer, added styrene monomer,
ous combinations of resins and layered particles. and polymerized the mixture using living polymeriza-
Studies on the in situ polymerization are still being tion to obtain a nanocomposite (Fig. 4. 4. 17) [8].
conducted, although reports have appeared recently in All of these layered particle nanocomposites have
which nanocomposites are obtained by mixing and improved mechanical properties such as tensile
kneading intercalated particles with polymers without strength and flexural modulus, thermal properties
polymerization [2, 3]. such as thermal deformation temperature and crystal-
The oldest study on preparing layered particle/ lization speed, and gas barrier.
polymer nanocomposite by polymerization is on Many reports have been published on nanoparticle
nanocomposite made from layered particles and in situ polymerization using particles other than
polyamide, in which nanocomposite is commercial- layered particles. For example, Choi et al. reported
ized [4]. Amine compounds can easily be inserted synthesis of PET and nylon Ag nanoparticle compos-
between layers by ion exchange; probably this is the ites [10]. In preparation of PET composite polymer,
reason why this combination was chosen for basic and oligomer was first produced from dimethyl terephtha-
commercialization studies. Many reports have been late and ethylene glycol (EG), and then to this
published on the preparation of polyamide nanocom- oligomer Ag nanoparticle EG slurry was added,
posite by intercalation polymerization. One of the finally the mixture was polymerized at 280°C for 3 h
methods Usuki et al. [1] reported is that montmoril- under reduced pressure. For nylon,
-caprolactam dis-
lonite is treated with 12-aminododecane acid and persed with Ag nanoparticle was reacted at 260°C for
214