Page 239 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 239
4.4 NANOCOMPOSITE STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS
In this report, Choi et al. considers simply that the
difference is due to the difference in affinity to water,
that is, the main chain of nylon is hydrophilic while
that of PET is hydrophobic. There is another consider-
ation that the dispersing agent may be desorbed from
the particles, but the metal particles may be stabilized
by the unshared electron pair on a nitrogen atom of the
amido group of the nylon main chain. That is, the
polymer itself may work as a dispersing agent.
Acrylic monomers are used in many studies on the
preparation of composite materials from metal parti-
cles and polymer precursors. For example, Fang et al.
dispersed synthesized CoPt nanoparticles with a mix-
ture of methyl methacrylate, ethylene glycol
dimethacrylate, and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate
monomers, then polymerized and cross-linked the
mixture by UV radiation to obtain CoPt–PMMA
nanocomposite [11]. Many reports have been pub-
lished on metal nanoparticle composite using acrylic
polymers.
(2) Simultaneous syntheses of particles and polymers
The Pechini process [12, 13] is a sol-gel method for
obtaining particles from a homogeneous mixture of
precursors of the particles, polycarboxylic acid, and
polyol (a precursor of polymer) that are capable of
forming complexes with the precursors of the parti-
cles. One example of syntheses is that citric acid, an
excess amount of ethylene glycol and a metallic salt
compound are mixed to obtain a homogeneous solu-
tion, and the mixture is esterified at 160–300°C.
Further polymerization reaction to increase the poly-
merization degree and particle formation reaction
such as hydrolysis were performed at the same time to
obtain gel-type polymer/particle composite [14, 15].
Studies have been published on the use ethylenedi-
amine tetraacetic acid instead of citric acid [13]. That
is, a feature of the Pechini method is to obtain homo-
geneous particles using chemical compounds capable
of forming easily stable complexes in the particle
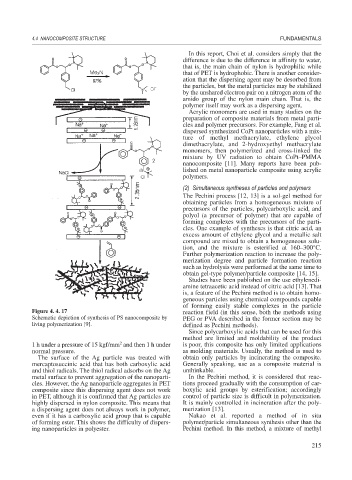
Figure 4. 4. 17 reaction field (in this sense, both the methods using
Schematic depiction of synthesis of PS nanocomposite by PEG or PVA described in the former section may be
living polymerization [9]. defined as Pechini methods).
Since polycarboxylic acids that can be used for this
method are limited and moldability of the product
2
1 h under a pressure of 15 kgf/mm and then 1 h under is poor, this composite has only limited applications
normal pressure. as molding materials. Usually, the method is used to
The surface of the Ag particle was treated with obtain only particles by incinerating the composite.
mercaptosuccinic acid that has both carboxylic acid Generally speaking, use as a composite material is
and thiol radicals. The thiol radical adsorbs on the Ag unthinkable.
metal surface to prevent aggregation of the nanoparti- In the Pechini method, it is considered that reac-
cles. However, the Ag nanoparticle aggregates in PET tions proceed gradually with the consumption of car-
composite since this dispersing agent does not work boxylic acid groups by esterification; accordingly
in PET, although it is confirmed that Ag particles are control of particle size is difficult in polymerization.
highly dispersed in nylon composite. This means that It is mainly controlled in incineration after the poly-
a dispersing agent does not always work in polymer, merization [13].
even if it has a carboxylic acid group that is capable Nakao et al. reported a method of in situ
of forming ester. This shows the difficulty of dispers- polymer/particle simultaneous synthesis other than the
ing nanoparticles in polyester. Pechini method. In this method, a mixture of methyl
215