Page 244 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 244
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 4 CONTROL OF NANOSTRUCTURE OF MATERIALS
4.4.6 Nanostructure control of alloy hardening makes it difficult to consolidate them.
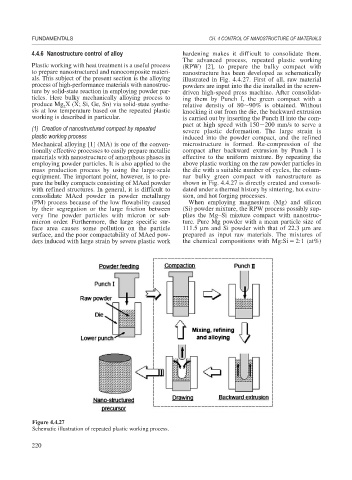
The advanced process, repeated plastic working
Plastic working with heat treatment is a useful process (RPW) [2], to prepare the bulky compact with
to prepare nanostructured and nanocomposite materi- nanostructure has been developed as schematically
als. This subject of the present section is the alloying illustrated in Fig. 4.4.27. First of all, raw material
process of high-performance materials with nanostruc- powders are input into the die installed in the screw-
ture by solid-state reaction in employing powder par- driven high-speed press machine. After consolidat-
ticles. Here bulky mechanically alloying process to ing them by Punch I, the green compact with a
produce Mg X (X; Si, Ge, Sn) via solid-state synthe- relative density of 80 90% is obtained. Without
2
sis at low temperature based on the repeated plastic knocking it out from the die, the backward extrusion
working is described in particular. is carried out by inserting the Punch II into the com-
pact at high speed with 150 200 mm/s to serve a
(1) Creation of nanostructured compact by repeated
severe plastic deformation. The large strain is
plastic working process induced into the powder compact, and the refined
Mechanical alloying [1] (MA) is one of the conven- microstructure is formed. Re-compression of the
tionally effective processes to easily prepare metallic compact after backward extrusion by Punch I is
materials with nanostructure of amorphous phases in effective to the uniform mixture. By repeating the
employing powder particles. It is also applied to the above plastic working on the raw powder particles in
mass production process by using the large-scale the die with a suitable number of cycles, the colum-
equipment. The important point, however, is to pre- nar bulky green compact with nanostructure as
pare the bulky compacts consisting of MAed powder shown in Fig. 4.4.27 is directly created and consoli-
with refined structures. In general, it is difficult to dated under a thermal history by sintering, hot extru-
consolidate MAed powder in powder metallurgy sion, and hot forging processes.
(PM) process because of the low flowability caused When employing magnesium (Mg) and silicon
by their segregation or the large friction between (Si) powder mixture, the RPW process possibly sup-
very fine powder particles with micron or sub- plies the Mg–Si mixture compact with nanostruc-
micron order. Furthermore, the large specific sur- ture. Pure Mg powder with a mean particle size of
face area causes some pollution on the particle 111.5
m and Si powder with that of 22.3
m are
surface, and the poor compactability of MAed pow- prepared as input raw materials. The mixtures of
ders induced with large strain by severe plastic work the chemical compositions with Mg:Si 2:1 (at%)
Figure 4.4.27
Schematic illustration of repeated plastic working process.
220