Page 245 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 245
4.4 NANOCOMPOSITE STRUCTURE FUNDAMENTALS
are supplied into the die with a inner diameter of
35 mm installed in the 1,000 kN screw-driven press
machine. After consolidating them by applying 600
MPa, Punch II with an outer diameter of 11 mm is
inserted into the compact for the backward extru-
sion. The maximum number of cycles is 600 in this
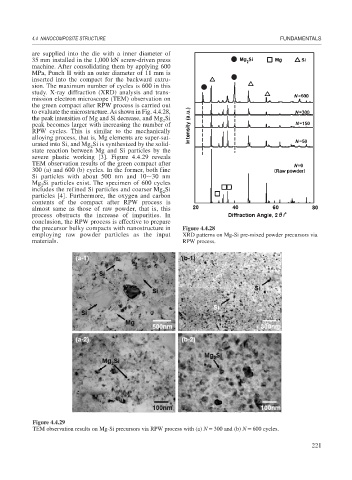
study. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis and trans-
mission electron microscope (TEM) observation on
the green compact after RPW process is carried out
to evaluate the microstructure. As shown in Fig. 4.4.28,
the peak intensities of Mg and Si decrease, and Mg Si
2
peak becomes larger with increasing the number of
RPW cycles. This is similar to the mechanically
alloying process, that is, Mg elements are super-sat-
urated into Si, and Mg Si is synthesized by the solid-
2
state reaction between Mg and Si particles by the
severe plastic working [3]. Figure 4.4.29 reveals
TEM observation results of the green compact after
300 (a) and 600 (b) cycles. In the former, both fine
Si particles with about 500 nm and 10 30 nm
Mg Si particles exist. The specimen of 600 cycles
2
includes the refined Si particles and coarser Mg Si
2
particles [4]. Furthermore, the oxygen and carbon
contents of the compact after RPW process is
almost same as those of raw powder, that is, this
process obstructs the increase of impurities. In
conclusion, the RPW process is effective to prepare
the precursor bulky compacts with nanostructure in Figure 4.4.28
employing raw powder particles as the input XRD patterns on Mg-Si pre-mixed powder precursors via
materials. RPW process.
Figure 4.4.29
TEM observation results on Mg-Si precursors via RPW process with (a) N 300 and (b) N 600 cycles.
221