Page 347 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 347
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 6 EVALUATION METHODS FOR PROPERTIES OF NANOSTRUCTURED BODY
1μm
Figure 6.1.3 Figure 6.1.4
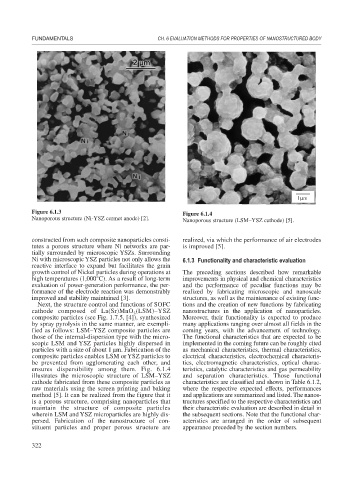
Nanoporous structure (Ni-YSZ cermet anode) [2]. Nanoporous structure (LSM–YSZ cathode) [5].
constructed from such composite nanoparticles consti- realized, via which the performance of air electrodes
tutes a porous structure where Ni networks are par- is improved [5].
tially surrounded by microscopic YSZs. Surrounding
Ni with microscopic YSZ particles not only allows the 6.1.3 Functionality and characteristic evaluation
reactive interface to expand but facilitates the grain
growth control of Nickel particles during operations at The preceding sections described how remarkable
high temperatures (1,000°C). As a result of long-term improvements in physical and chemical characteristics
evaluation of power-generation performance, the per- and the performance of peculiar functions may be
formance of the electrode reaction was demonstrably realized by fabricating microscopic and nanoscale
improved and stability maintained [3]. structures, as well as the maintenance of existing func-
Next, the structure control and functions of SOFC tions and the creation of new functions by fabricating
cathode composed of La(Sr)MnO (LSM)–YSZ nanostructures in the application of nanoparticles.
3
composite particles (see Fig. 1.7.5, [4]), synthesized Moreover, their functionality is expected to produce
by spray pyrolysis in the same manner, are exempli- many applications ranging over almost all fields in the
fied as follows: LSM–YSZ composite particles are coming years, with the advancement of technology.
those of the internal-dispersion type with the micro- The functional characteristics that are expected to be
scopic LSM and YSZ particles highly dispersed in implemented in the coming future can be roughly cited
particles with a size of about 1 m. Fabrication of the as mechanical characteristics, thermal characteristics,
composite particles enables LSM or YSZ particles to electrical characteristics, electrochemical characteris-
be prevented from agglomerating each other, and tics, electromagnetic characteristics, optical charac-
ensures dispersibility among them. Fig. 6.1.4 teristics, catalytic characteristics and gas permeability
illustrates the microscopic structure of LSM–YSZ and separation characteristics. Those functional
cathode fabricated from these composite particles as characteristics are classified and shown in Table 6.1.2,
raw materials using the screen printing and baking where the respective expected effects, performances
method [5]. It can be realized from the figure that it and applications are summarized and listed. The nanos-
is a porous structure, comprising nanoparticles that tructures specified to the respective characteristics and
maintain the structure of composite particles their characteristic evaluation are described in detail in
wherein LSM and YSZ microparticles are highly dis- the subsequent sections. Note that the functional char-
persed. Fabrication of the nanostructure of con- acteristics are arranged in the order of subsequent
stituent particles and proper porous structure are appearance preceded by the section numbers.
322