Page 496 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 496
APPLICATIONS 12 ZEOLITE MEMBRANE
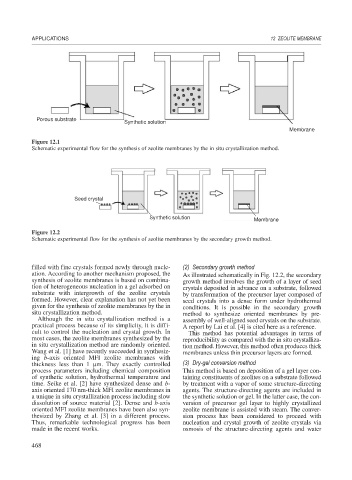
Porous substrate
Synthetic solution
Membrane
Figure 12.1
Schematic experimental flow for the synthesis of zeolite membranes by the in situ crystallization method.
Seed crystal
Synthetic solution
Membrane
Figure 12.2
Schematic experimental flow for the synthesis of zeolite membranes by the secondary growth method.
filled with fine crystals formed newly through nucle- (2) Secondary growth method
ation. According to another mechanism proposed, the As illustrated schematically in Fig. 12.2, the secondary
synthesis of zeolite membranes is based on combina- growth method involves the growth of a layer of seed
tion of heterogeneous nucleation in a gel adsorbed on crystals deposited in advance on a substrate, followed
substrate with intergrowth of the zeolite crystals by transformation of the precursor layer composed of
formed. However, clear explanation has not yet been seed crystals into a dense form under hydrothermal
given for the synthesis of zeolite membranes by the in conditions. It is possible in the secondary growth
situ crystallization method. method to synthesize oriented membranes by pre-
Although the in situ crystallization method is a assembly of well-aligned seed crystals on the substrate.
practical process because of its simplicity, it is diffi- A report by Lai et al. [4] is cited here as a reference.
cult to control the nucleation and crystal growth. In This method has potential advantages in terms of
most cases, the zeolite membranes synthesized by the reproducibility as compared with the in situ crystalliza-
in situ crystallization method are randomly oriented. tion method. However, this method often produces thick
Wang et al. [1] have recently succeeded in synthesiz- membranes unless thin precursor layers are formed.
ing b-axis oriented MFI zeolite membranes with
thickness less than 1 m. They exactly controlled (3) Dry-gel conversion method
process parameters including chemical composition This method is based on deposition of a gel layer con-
of synthetic solution, hydrothermal temperature and taining constituents of zeolites on a substrate followed
time. Seike et al. [2] have synthesized dense and b- by treatment with a vapor of some structure-directing
axis oriented 170 nm-thick MFI zeolite membranes in agents. The structure-directing agents are included in
a unique in situ crystallization process including slow the synthetic solution or gel. In the latter case, the con-
dissolution of source material [2]. Dense and b-axis version of precursor gel layer to highly crystallized
oriented MFI zeolite membranes have been also syn- zeolite membrane is assisted with steam. The conver-
thesized by Zhang et al. [3] in a different process. sion process has been considered to proceed with
Thus, remarkable technological progress has been nucleation and crystal growth of zeolite crystals via
made in the recent works. osmosis of the structure-directing agents and water
468