Page 39 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 39
1.2 DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND THE PROBLEM OF ADAPTABILITY 27
u
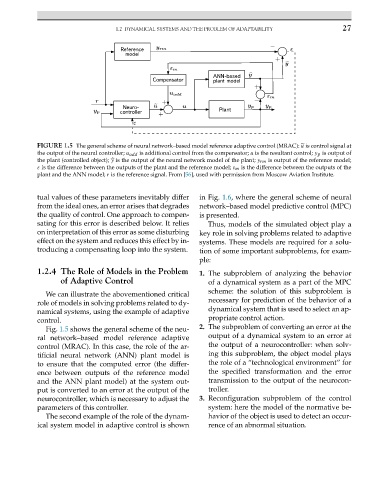
FIGURE 1.5 The general scheme of neural network–based model reference adaptive control (MRAC): is control signal at
the output of the neural controller; u add is additional control from the compensator; u is the resultant control; y p is output of
y
the plant (controlled object); is the output of the neural network model of the plant; y rm is output of the reference model;
ε is thedifferencebetween theoutputs of theplant andthereferencemodel; ε m is the difference between the outputs of the
plant and the ANN model; r is the reference signal. From [56], used with permission from Moscow Aviation Institute.
tual values of these parameters inevitably differ in Fig. 1.6, where the general scheme of neural
from the ideal ones, an error arises that degrades network–based model predictive control (MPC)
the quality of control. One approach to compen- is presented.
sating for this error is described below. It relies Thus, models of the simulated object play a
on interpretation of this error as some disturbing key role in solving problems related to adaptive
effect on the system and reduces this effect by in- systems. These models are required for a solu-
troducing a compensating loop into the system. tion of some important subproblems, for exam-
ple:
1.2.4 The Role of Models in the Problem 1. The subproblem of analyzing the behavior
of Adaptive Control of a dynamical system as a part of the MPC
scheme: the solution of this subproblem is
We can illustrate the abovementioned critical
necessary for prediction of the behavior of a
role of models in solving problems related to dy-
namical systems, using the example of adaptive dynamical system that is used to select an ap-
control. propriate control action.
Fig. 1.5 shows the general scheme of the neu- 2. The subproblem of converting an error at the
ral network–based model reference adaptive output of a dynamical system to an error at
control (MRAC). In this case, the role of the ar- the output of a neurocontroller: when solv-
tificial neural network (ANN) plant model is ing this subproblem, the object model plays
to ensure that the computed error (the differ- the role of a “technological environment” for
ence between outputs of the reference model the specified transformation and the error
and the ANN plant model) at the system out- transmission to the output of the neurocon-
put is converted to an error at the output of the troller.
neurocontroller, which is necessary to adjust the 3. Reconfiguration subproblem of the control
parameters of this controller. system: here the model of the normative be-
The second example of the role of the dynam- havior of the object is used to detect an occur-
ical system model in adaptive control is shown rence of an abnormal situation.