Page 91 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 91
2.4 TRAINING SET ACQUISITION PROBLEM FOR DYNAMIC NEURAL NETWORKS 79
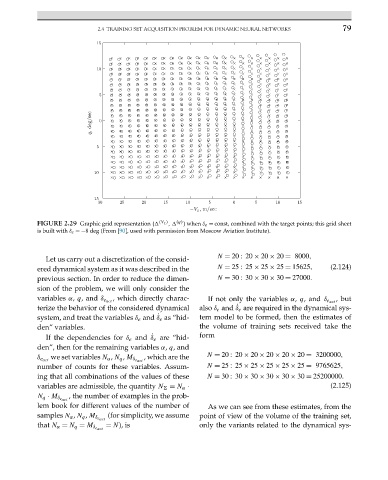
FIGURE 2.29 Graphic grid representation { (V z ) , (q) } when δ e = const, combined with the target points; this grid sheet
is built with δ e =−8 deg (From [90], used with permission from Moscow Aviation Institute).
N = 20 : 20 × 20 × 20 = 8000,
Let us carry out a discretization of the consid-
ered dynamical system as it was described in the N = 25 : 25 × 25 × 25 = 15625, (2.124)
previous section. In order to reduce the dimen- N = 30 : 30 × 30 × 30 = 27000.
sion of the problem, we will only consider the
, which directly charac- ,but
variables α, q,and δ e act If not only the variables α, q,and δ e act
terize the behavior of the considered dynamical also δ e and ˙ δ e are required in the dynamical sys-
system, and treat the variables δ e and δ e as “hid- tem model to be formed, then the estimates of
˙
den” variables. the volume of training sets received take the
If the dependencies for δ e and δ e are “hid- form
˙
den”, then for the remaining variables α, q,and
, which are the N = 20 : 20 × 20 × 20 × 20 × 20 = 3200000,
δ e act we set variables N α , N q , M δ e act
number of counts for these variables. Assum- N = 25 : 25 × 25 × 25 × 25 × 25 = 9765625,
ing that all combinations of the values of these N = 30 : 30 × 30 × 30 × 30 × 30 = 25200000.
variables are admissible, the quantity N = N α · (2.125)
, the number of examples in the prob-
N q · M δ e act
lem book for different values of the number of As we can see from these estimates, from the
(for simplicity, we assume point of view of the volume of the training set,
samples N α , N q , M δ e act
= N), is only the variants related to the dynamical sys-
that N α = N q = M δ e act