Page 108 - New Trends In Coal Conversion
P. 108
Minimization of Hg and trace elements during coal combustion and gasification processes 71
0
Hg (g)
Catalytic
oxidation
2+
Hg X(g)
Chlorination
HgCl (g) HgCl (g)
2
2
Hg(p) species
HgCl 2
0
Hg (g) Sorption HgO
HgSO 4
HgS
Vaporization
Ash
formation
Coal Combustion Postcombustion
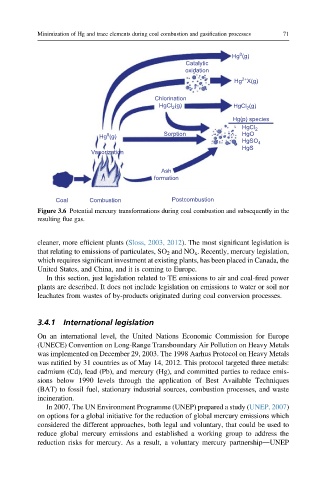
Figure 3.6 Potential mercury transformations during coal combustion and subsequently in the
resulting flue gas.
cleaner, more efficient plants (Sloss, 2003, 2012). The most significant legislation is
that relating to emissions of particulates, SO 2 and NO x . Recently, mercury legislation,
which requires significant investment at existing plants, has been placed in Canada, the
United States, and China, and it is coming to Europe.
In this section, just legislation related to TE emissions to air and coal-fired power
plants are described. It does not include legislation on emissions to water or soil nor
leachates from wastes of by-products originated during coal conversion processes.
3.4.1 International legislation
On an international level, the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe
(UNECE) Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution on Heavy Metals
was implemented on December 29, 2003. The 1998 Aarhus Protocol on Heavy Metals
was ratified by 31 countries as of May 14, 2012. This protocol targeted three metals:
cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), and mercury (Hg), and committed parties to reduce emis-
sions below 1990 levels through the application of Best Available Techniques
(BAT) to fossil fuel, stationary industrial sources, combustion processes, and waste
incineration.
In 2007, The UN Environment Programme (UNEP) prepared a study (UNEP, 2007)
on options for a global initiative for the reduction of global mercury emissions which
considered the different approaches, both legal and voluntary, that could be used to
reduce global mercury emissions and established a working group to address the
reduction risks for mercury. As a result, a voluntary mercury partnershipdUNEP