Page 99 - New Trends In Coal Conversion
P. 99
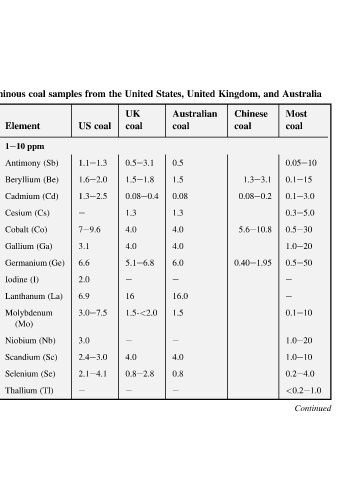
Australia Most coal 0.05e10 0.1e15 0.1e3.0 0.3e5.0 0.5e30 1.0e20 0.5e50 e e 0.1e10 1.0e20 1.0e10 0.2e4.0 <0.2e1.0 Continued
and 1.3e3.1 0.08e0.2 5.6e10.8
Kingdom, Chinese coal 0.40e1.95
United Australian
States, coal 0.5 1.5 0.08 1.3 4.0 4.0 6.0 e 16.0 1.5 e 4.0 0.8 e
United UK coal 0.5e3.1 1.5e1.8 0.08e0.4 1.3 4.0 4.0 5.1e6.8 e 16 1.5-<2.0 e 4.0 0.8e2.8 e
the
from coal US 1.1e1.3 1.6e2.0 1.3e2.5 e 7e9.6 3.1 6.6 2.0 6.9 3.0e7.5 3.0 2.4e3.0 2.1e4.1 e
samples (Sb) (Be) (La) (Sc)
coal Element 1e10 ppm Antimony Beryllium (Cd) Cadmium (Cs) Cesium (Co) Cobalt (Ga) Gallium Germanium (Ge) (I) Iodine Lanthanum Molybdenum (Mo) (Nb) Niobium Scandium (Se) Selenium (Tl) Thallium
subbituminous 20e1000 20e500 10e3000 15e500 10e2000 50e200
and Most coal 5e400 5e300 5e300 0.5e80 e e 0.5e60
bituminous Chinese coal 9.6e21.0 12.0e74.0
1500
in Australian coal 70e300 30e60 150 130 100 900 1.588 150 6.0
elements e 25 e e
trace UK coal 70e300 30e60 114e150 84e130 e 100 63e900 25 1.5e18 e e 150 6e34
of coal
Concentrations US 150 50e102 61e74 49e100 (Mn) 71 (P) 37e100 700e800 39e272 14e15 11 15 e 14e15
3.1 (Ba) (B) (F) Manganese Phosphorous (Sr) (Ti) (Zn) ppm (As) (Ce) (Br) (Cl) (Cr) Chromium
Table Element >50 ppm Barium Boron Fluorine Strontium Titanium Zinc 10e50 Arsenic Cerium Bromine Chlorine