Page 162 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 162
134 New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete
The chemical composition revealed a high amount of Ca, Mg, Na, P and K.
Usually, increasing the calcination temperature increases the concentration of
these elements. Other elements were present as minor quantities, and some ele-
ments, such as Pb and Cd, showed up as highly volatile elements. Thus, the con-
centration of these last elements decreased from 300 to 800 C. In this paper, a
SEM study was carried out to characterise the ashes. A large amount of organic
matter was observed in the micrographs of the ash at 300 C, whereas that matter
disappeared in the ashes obtained at 500 C. Generally, all the samples showed
the presence of some crystalline aggregates and amorphous phases with an irreg-
ular morphology. The XRD showed the presence of quartz and calcite as the
main minerals. Also, dolomite, anhydrite and phosphorous compounds were iden-
tified. In the ash calcined at 800 C, free-lime due the calcite decomposition was
detected and complex additional phases were formed that had a chemical struc-
ture close to wilkeite.
Recently, Kappel et al. (2017) studied the colour, compressive strength and
workability of mortar when cement was partly replaced by iron-rich SSA that was
ground into six different fractions. SSA was collected at a wastewater treatment
plant in Copenhagen (Denmark) and incinerated in a fluidised bed combustor at
850 C. In the treatment plant, phosphorous was removed by chemical precipitation
with iron salts. Thus, the SSA had a red iron-oxide colour. The SSA was a mixture
of at least 95% of the ash captured in the electrostatic filter and 5% of
residues from the filter bag. The pH of the SSA was 9.9 (very alkaline) and it had a
water-soluble fraction of 1.5%. The chemical composition and trace metals are
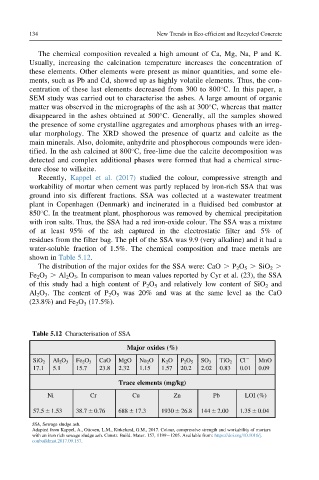
shown in Table 5.12.
The distribution of the major oxides for the SSA were: CaO . P 2 O 5 . SiO 2 .
Fe 2 O 3 . Al 2 O 3 . In comparison to mean values reported by Cyr et al. (23), the SSA
of this study had a high content of P 2 O 5 and relatively low content of SiO 2 and
Al 2 O 3 . The content of P 2 O 5 was 20% and was at the same level as the CaO
(23.8%) and Fe 2 O 3 (17.5%).
Table 5.12 Characterisation of SSA
Major oxides (%)
CaO MgO Na 2 O K 2 O Cl 2 MnO
SiO 2 Al 2 O 3 Fe 2 O 3 P 2 O 5 SO 3 TiO 2
17.1 5.1 15.7 23.8 2.32 1.15 1.57 20.2 2.02 0.83 0.01 0.09
Trace elements (mg/kg)
Ni Cr Cu Zn Pb LOI (%)
57.5 6 1.53 38.7 6 0.76 688 6 17.3 1930 6 26.8 144 6 2.00 1.35 6 0.04
SSA, Sewage sludge ash.
Adapted from Kappel, A., Ottosen, L.M., Kirkelund, G.M., 2017. Colour, compressive strength and workability of mortars
with an iron rich sewage sludge ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 157, 1199 1205. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.
conbuildmat.2017.09.157.