Page 244 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 244
212 New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete
Production of Production of
fuels and
electricity raw materials
Production of
Production of
fuels and raw materials Primary Iron blast
Primary electricity production furnace Iron
production transformation
Production of Coal fired Production of Slag
water power plant Bottom ash water granulation
Steel
Electrical
Treatment power network Treatment Drying
Drying
Electricity
Grinding
Stock
Stock
Fly ash GBFS
Extraction of raw
materials
Primary
production
Production of fuels Combustion in the Si-metal
and energy electric arc oven
Treatment
Stock
Silica fume
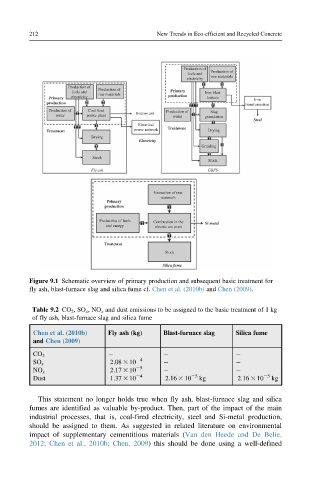
Figure 9.1 Schematic overview of primary production and subsequent basic treatment for
fly ash, blast-furnace slag and silica fume cf. Chen et al. (2010b) and Chen (2009).
Table 9.2 CO 2 ,SO x ,NO x and dust emissions to be assigned to the basic treatment of 1 kg
of fly ash, blast-furnace slag and silica fume
Chen et al. (2010b) Fly ash (kg) Blast-furnace slag Silica fume
and Chen (2009)
CO 2
2.08 3 10 24
SO x
2.17 3 10 25
NO x
Dust 1.37 3 10 24 2.16 3 10 25 kg 2.16 3 10 25 kg
This statement no longer holds true when fly ash, blast-furnace slag and silica
fumes are identified as valuable by-product. Then, part of the impact of the main
industrial processes, that is, coal-fired electricity, steel and Si-metal production,
should be assigned to them. As suggested in related literature on environmental
impact of supplementary cementitious materials (Van den Heede and De Belie,
2012; Chen et al., 2010b; Chen, 2009) this should be done using a well-defined