Page 418 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 418
372 New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete
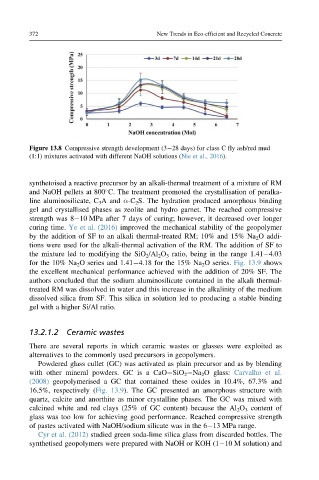
Figure 13.8 Compressive strength development (3 28 days) for class C fly ash/red mud
(1:1) mixtures activated with different NaOH solutions (Nie et al., 2016).
synthetoised a reactive precursor by an alkali-thermal treatment of a mixture of RM
and NaOH pellets at 800 C. The treatment promoted the crystallisation of peralka-
line aluminosilicate, C 3 A and α-C 2 S. The hydration produced amorphous binding
gel and crystallised phases as zeolite and hydro garnet. The reached compressive
strength was 8 10 MPa after 7 days of curing; however, it decreased over longer
curing time. Ye et al. (2016) improved the mechanical stability of the geopolymer
by the addition of SF to an alkali thermal-treated RM; 10% and 15% Na 2 O addi-
tions were used for the alkali-thermal activation of the RM. The addition of SF to
the mixture led to modifying the SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 ratio, being in the range 1.41 4.03
for the 10% Na 2 O series and 1.41 4.18 for the 15% Na 2 O series. Fig. 13.9 shows
the excellent mechanical performance achieved with the addition of 20% SF. The
authors concluded that the sodium aluminosilicate contained in the alkali thermal-
treated RM was dissolved in water and this increase in the alkalinity of the medium
dissolved silica from SF. This silica in solution led to producing a stable binding
gel with a higher Si/Al ratio.
13.2.1.2 Ceramic wastes
There are several reports in which ceramic wastes or glasses were exploited as
alternatives to the commonly used precursors in geopolymers.
Powdered glass cullet (GC) was activated as plain precursor and as by blending
with other mineral powders. GC is a CaO SiO 2 Na 2 O glass: Carvalho et al.
(2008) geopolymerised a GC that contained these oxides in 10.4%, 67.3% and
16.5%, respectively (Fig. 13.9). The GC presented an amorphous structure with
quartz, calcite and anorthite as minor crystalline phases. The GC was mixed with
calcined white and red clays (25% of GC content) because the Al 2 O 3 content of
glass was too low for achieving good performance. Reached compressive strength
of pastes activated with NaOH/sodium silicate was in the 6 13 MPa range.
Cyr et al. (2012) studied green soda-lime silica glass from discarded bottles. The
synthetised geopolymers were prepared with NaOH or KOH (1 10 M solution) and