Page 421 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 421
Application of alkali-activated industrial waste 375
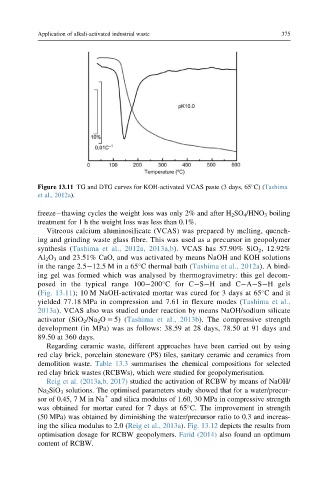
Figure 13.11 TG and DTG curves for KOH-activated VCAS paste (3 days, 65 C) (Tashima
et al., 2012a).
freeze thawing cycles the weight loss was only 2% and after H 2 SO 4 /HNO 3 boiling
treatment for 1 h the weight loss was less than 0.1%.
Vitreous calcium aluminosilicate (VCAS) was prepared by melting, quench-
ing and grinding waste glass fibre. This was used as a precursor in geopolymer
synthesis (Tashima et al., 2012a, 2013a,b). VCAS has 57.90% SiO 2 , 12.92%
Al 2 O 3 and 23.51% CaO, and was activated by means NaOH and KOH solutions
in the range 2.5 12.5 M in a 65 C thermal bath (Tashima et al., 2012a). A bind-
inggel wasformedwhich wasanalysedby thermogravimetry: this gel decom-
posed in the typical range 100 200 Cfor C S Hand C A S Hgels
(Fig. 13.11); 10 M NaOH-activated mortar was cured for 3 days at 65 Cand it
yielded 77.18 MPa in compression and 7.61 in flexure modes (Tashima et al.,
2013a). VCAS also was studied under reaction by means NaOH/sodium silicate
activator (SiO 2 /Na 2 O 5 5) (Tashima et al., 2013b). The compressive strength
development (in MPa) was as follows: 38.59 at 28 days, 78.50 at 91 days and
89.50 at 360 days.
Regarding ceramic waste, different approaches have been carried out by using
red clay brick, porcelain stoneware (PS) tiles, sanitary ceramic and ceramics from
demolition waste. Table 13.3 summarises the chemical compositions for selected
red clay brick wastes (RCBWs), which were studied for geopolymerisation.
Reig et al. (2013a,b, 2017) studied the activation of RCBW by means of NaOH/
Na 2 SiO 3 solutions. The optimised parameters study showed that for a water/precur-
1
sor of 0.45, 7 M in Na and silica modulus of 1.60, 30 MPa in compressive strength
was obtained for mortar cured for 7 days at 65 C. The improvement in strength
(50 MPa) was obtained by diminishing the water/precursor ratio to 0.3 and increas-
ing the silica modulus to 2.0 (Reig et al., 2013a). Fig. 13.12 depicts the results from
optimisation dosage for RCBW geopolymers. Farid (2014) also found an optimum
content of RCBW.