Page 475 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 475
Microstructural studies on 14
recycled aggregate concrete
Luı´s Evangelista 1,2 and M. Guedes 3,4
1
ISEL-IPL, Department of Civil Engineering, Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa,
2
3
Lisboa, Portugal, CERIS-ICIST, Instituto Superior Te ´cnico, Lisboa, Portugal, CDP2T and
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Setu ´bal School of Technology, Instituto
4
Polite ´cnico de Setu ´bal, Setu ´bal, Portugal, CeFEMA, Instituto Superior Te ´cnico, Lisboa,
Portugal
14.1 Introduction
Concrete is commonly understood as a three-phase composite material comprising
hardened cement paste, the aggregate structure and the interfacial transition zone
(ITZ) between the hardened cement paste and the aggregate surface. The resulting
microstructure is extremely complex and presents features (including pores) over
several length scales (Garboczi, 1993), ranging from nanometric (e.g., C S H)
and micrometric (e.g., unhydrated cement particles, calcium hydroxide (CH) or the
ITZ) components, to the millimetric random structure of cement paste/sand
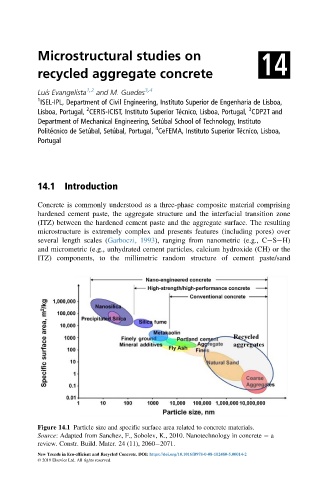
Figure 14.1 Particle size and specific surface area related to concrete materials.
Source: Adapted from Sanchez, F., Sobolev, K., 2010. Nanotechnology in concrete a
review. Constr. Build. Mater. 24 (11), 2060 2071.
New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102480-5.00014-2
© 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.