Page 61 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 61
Biomass fly ash and biomass bottom ash 37
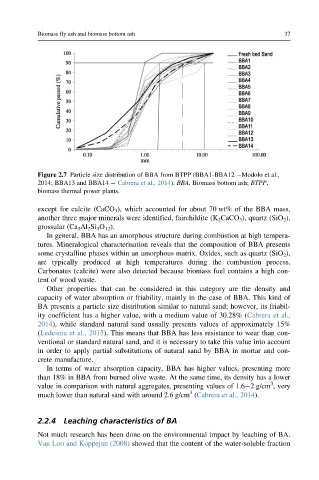
Figure 2.7 Particle size distribution of BBA from BTPP (BBA1-BBA12 Modolo et al.,
2014; BBA13 and BBA14 Cabrera et al., 2014). BBA, Biomass bottom ash; BTPP,
biomass thermal power plants.
except for calcite (CaCO 3 ), which accounted for about 70 wt% of the BBA mass,
another three major minerals were identified, fairchildite (K 2 CaCO 3 ), quartz (SiO 2 ),
grossular (Ca 3 Al 2 Si 3 O 12 ).
In general, BBA has an amorphous structure during combustion at high tempera-
tures. Mineralogical characterisation reveals that the composition of BBA presents
some crystalline phases within an amorphous matrix. Oxides, such as quartz (SiO 2 ),
are typically produced at high temperatures during the combustion process.
Carbonates (calcite) were also detected because biomass fuel contains a high con-
tent of wood waste.
Other properties that can be considered in this category are the density and
capacity of water absorption or friability, mainly in the case of BBA. This kind of
BA presents a particle size distribution similar to natural sand; however, its friabil-
ity coefficient has a higher value, with a medium value of 30.28% (Cabrera et al.,
2014), while standard natural sand usually presents values of approximately 15%
(Ledesma et al., 2015). This means that BBA has less resistance to wear than con-
ventional or standard natural sand, and it is necessary to take this value into account
in order to apply partial substitutions of natural sand by BBA in mortar and con-
crete manufacture.
In terms of water absorption capacity, BBA has higher values, presenting more
than 18% in BBA from burned olive waste. At the same time, its density has a lower
3
value in comparison with natural aggregates, presenting values of 1.6 2g/cm ,very
3
much lower than natural sand with around 2.6 g/cm (Cabrera et al., 2014).
2.2.4 Leaching characteristics of BA
Not much research has been done on the environmental impact by leaching of BA.
Van Loo and Koppejan (2008) showed that the content of the water-soluble fraction