Page 63 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 63
Biomass fly ash and biomass bottom ash 39
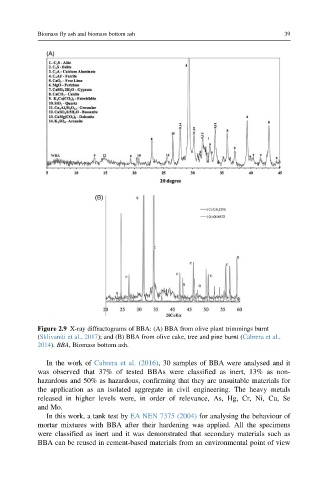
Figure 2.9 X-ray diffractograms of BBA: (A) BBA from olive plant trimmings burnt
(Sklivaniti et al., 2017); and (B) BBA from olive cake, tree and pine burnt (Cabrera et al.,
2014). BBA, Biomass bottom ash.
In the work of Cabrera et al. (2016), 30 samples of BBA were analysed and it
was observed that 37% of tested BBAs were classified as inert, 13% as non-
hazardous and 50% as hazardous, confirming that they are unsuitable materials for
the application as an isolated aggregate in civil engineering. The heavy metals
released in higher levels were, in order of relevance, As, Hg, Cr, Ni, Cu, Se
and Mo.
In this work, a tank test by EA NEN 7375 (2004) for analysing the behaviour of
mortar mixtures with BBA after their hardening was applied. All the specimens
were classified as inert and it was demonstrated that secondary materials such as
BBA can be reused in cement-based materials from an environmental point of view