Page 110 - Numerical Analysis and Modelling in Geomechanics
P. 110
WAVE-SEABED-STRUCTURE INTERACTION 91
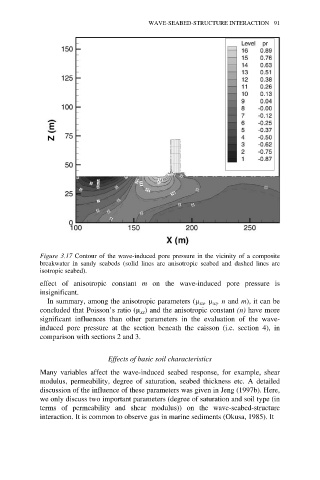
Figure 3.17 Contour of the wave-induced pore pressure in the vicinity of a composite
breakwater in sandy seabeds (solid lines are anisotropic seabed and dashed lines are
isotropic seabed).
effect of anisotropic constant m on the wave-induced pore pressure is
insignificant.
In summary, among the anisotropic parameters (µ , µ , n and m), it can be
xx
xz
concluded that Poisson’s ratio (µ ) and the anisotropic constant (n) have more
xx
significant influences than other parameters in the evaluation of the wave-
induced pore pressure at the section beneath the caisson (i.e. section 4), in
comparison with sections 2 and 3.
Effects of basic soil characteristics
Many variables affect the wave-induced seabed response, for example, shear
modulus, permeability, degree of saturation, seabed thickness etc. A detailed
discussion of the influence of these parameters was given in Jeng (1997b). Here,
we only discuss two important parameters (degree of saturation and soil type (in
terms of permeability and shear modulus)) on the wave-seabed-structure
interaction. It is common to observe gas in marine sediments (Okusa, 1985). It