Page 361 - Numerical Analysis and Modelling in Geomechanics
P. 361
342 RESERVOIR COMPACTION, SUBSIDENCE AND WELL DAMAGE
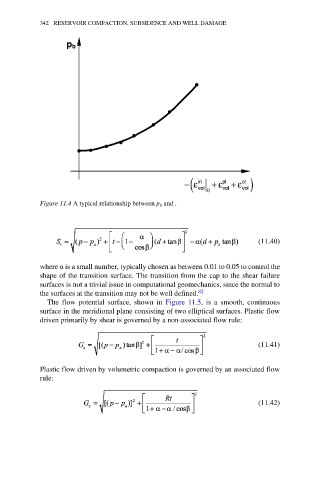
Figure 11.4 A typical relationship between p b and .
(11.40)
where α is a small number, typically chosen as between 0.01 to 0.05 to control the
shape of the transition surface. The transition from the cap to the shear failure
surfaces is not a trivial issue in computational geomechanics, since the normal to
82
the surfaces at the transition may not be well defined.
The flow potential surface, shown in Figure 11.5, is a smooth, continuous
surface in the meridional plane consisting of two elliptical surfaces. Plastic flow
driven primarily by shear is governed by a non-associated flow rule:
(11.41)
Plastic flow driven by volumetric compaction is governed by an associated flow
rule:
(11.42)