Page 50 - Oil and Gas Production Handbook An Introduction to Oil and Gas Production
P. 50
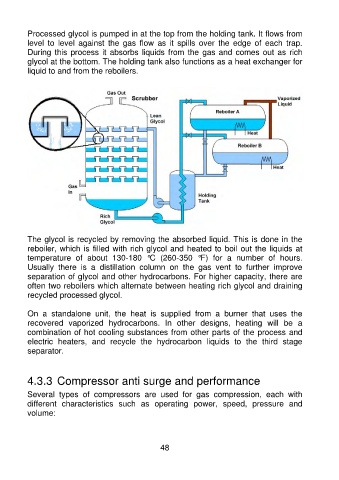
Processed glycol is pumped in at the top from the holding tank. It flows from
level to level against the gas flow as it spills over the edge of each trap.
During this process it absorbs liquids from the gas and comes out as rich
glycol at the bottom. The holding tank also functions as a heat exchanger for
liquid to and from the reboilers.
The glycol is recycled by removing the absorbed liquid. This is done in the
reboiler, which is filled with rich glycol and heated to boil out the liquids at
temperature of about 130-180 °C (260-350 °F) for a number of hours.
Usually there is a distillation column on the gas vent to further improve
separation of glycol and other hydrocarbons. For higher capacity, there are
often two reboilers which alternate between heating rich glycol and draining
recycled processed glycol.
On a standalone unit, the heat is supplied from a burner that uses the
recovered vaporized hydrocarbons. In other designs, heating will be a
combination of hot cooling substances from other parts of the process and
electric heaters, and recycle the hydrocarbon liquids to the third stage
separator.
4.3.3 Compressor anti surge and performance
Several types of compressors are used for gas compression, each with
different characteristics such as operating power, speed, pressure and
volume:
48