Page 49 - Oil and Gas Production Handbook An Introduction to Oil and Gas Production
P. 49
times the volume over the temperature (PV/T) must remain constant. (PV =
nkT). This ends up as a temperature increase.
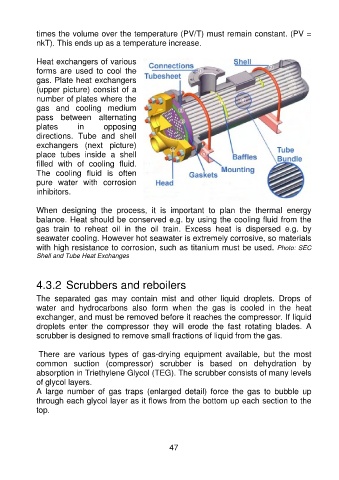
Heat exchangers of various
forms are used to cool the
gas. Plate heat exchangers
(upper picture) consist of a
number of plates where the
gas and cooling medium
pass between alternating
plates in opposing
directions. Tube and shell
exchangers (next picture)
place tubes inside a shell
filled with of cooling fluid.
The cooling fluid is often
pure water with corrosion
inhibitors.
When designing the process, it is important to plan the thermal energy
balance. Heat should be conserved e.g. by using the cooling fluid from the
gas train to reheat oil in the oil train. Excess heat is dispersed e.g. by
seawater cooling. However hot seawater is extremely corrosive, so materials
with high resistance to corrosion, such as titanium must be used. Photo: SEC
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanges
4.3.2 Scrubbers and reboilers
The separated gas may contain mist and other liquid droplets. Drops of
water and hydrocarbons also form when the gas is cooled in the heat
exchanger, and must be removed before it reaches the compressor. If liquid
droplets enter the compressor they will erode the fast rotating blades. A
scrubber is designed to remove small fractions of liquid from the gas.
There are various types of gas-drying equipment available, but the most
common suction (compressor) scrubber is based on dehydration by
absorption in Triethylene Glycol (TEG). The scrubber consists of many levels
of glycol layers.
A large number of gas traps (enlarged detail) force the gas to bubble up
through each glycol layer as it flows from the bottom up each section to the
top.
47