Page 212 - Op Amps Design, Applications, and Troubleshooting
P. 212
194 OSCILLATORS
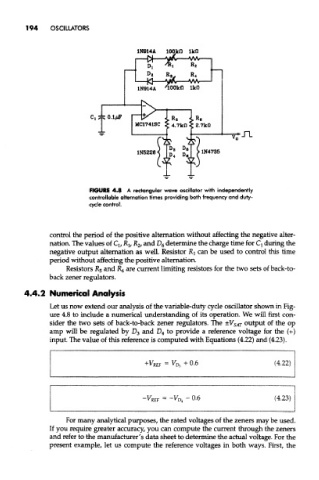
FIGURE 4.8 A rectangular wave oscillator with independently
controllable alternation times providing both frequency and duty-
cycle control.
control the period of the positive alternation without affecting the negative alter-
nation. The values of Q, R lf R 2, and D 6 determine the charge time for Q during the
negative output alternation as well. Resistor R } can be used to control this time
period without affecting the positive alternation.
Resistors R 5 and R 6 are current limiting resistors for the two sets of back-to-
back zener regulators.
4.4.2 Numerical Analysis
Let us now extend our analysis of the variable-duty cycle oscillator shown in Fig-
ure 4.8 to include a numerical understanding of its operation. We will first con-
sider the two sets of back-to-back zener regulators. The ±V SAT output of the op
amp will be regulated by D 3 and D 4 to provide a reference voltage for the (+)
input. The value of this reference is computed with Equations (4.22) and (4.23).
For many analytical purposes, the rated voltages of the zeners may be used.
If you require greater accuracy, you can compute the current through the zeners
and refer to the manufacturer's data sheet to determine the actual voltage. For the
present example, let us compute the reference voltages in both ways. First, the