Page 51 - Op Amps Design, Applications, and Troubleshooting
P. 51
34 BASIC CONCEPTS OF THE INTEGRATED OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
SUMMARY
Operational amplifiers are integrated circuits that contain complete functional
amplifier circuits whose electrical characteristics can be altered by external feed-
back. The input circuitry and essentially the heart of an op amp is the differential
amplifier circuit. An op amp responds to the difference in potential on its two
input terminals.
Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws are essential tools for the analysis of op amp cir-
cuits. Additionally/ simplification methods such as Thevenin's Theorem, Norton's
Theorem, and the Superposition Theorem can simplify the analysis of otherwise
complex op amp circuits.
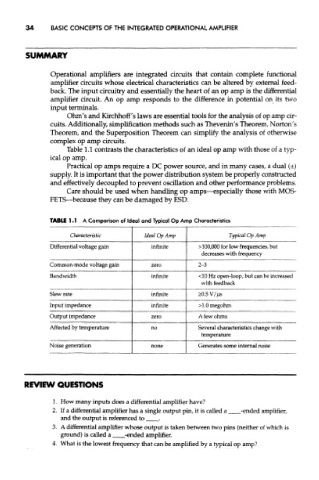
Table 1.1 contrasts the characteristics of an ideal op amp with those of a typ-
ical op amp.
Practical op amps require a DC power source, and in many cases, a dual (±)
supply. It is important that the power distribution system be properly constructed
and effectively decoupled to prevent oscillation and other performance problems.
Care should be used when handling op amps—especially those with MOS-
FETS—because they can be damaged by BSD.
TABLE 1.1 A Comparison of Ideal and Typical Op Amp Characteristics
Characteristic Ideal Op Amp Typical Op Amp
Differential voltage gain infinite > 100,000 for low frequencies, but
decreases with frequency
Common-mode voltage gain zero 2-3
Bandwidth infinite <10 Hz open-loop, but can be increased
with feedback
Slew rate infinite >0.5 V//is
Input impedance infinite >1.0 megohm
Output impedance zero A few ohms
Affected by temperature no Several characteristics change with
temperature
Noise generation none Generates some internal noise
REVIEW QUESTIONS
1. How many inputs does a differential amplifier have?
2. If a differential amplifier has a single output pin, it is called a -ended amplifier,
and the output is referenced to .
3. A differential amplifier whose output is taken between two pins (neither of which is
ground) is called a -ended amplifier.
4. What is the lowest frequency that can be amplified by a typical op amp?