Page 62 - Op Amps Design, Applications, and Troubleshooting
P. 62
Inverting Amplifier 45
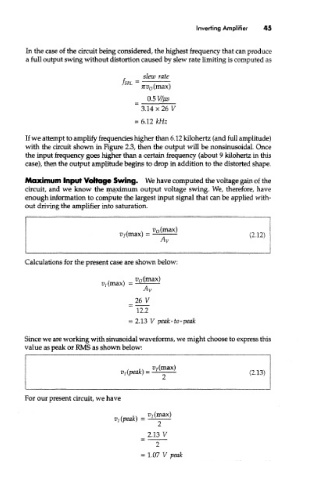
In the case of the circuit being considered, the highest frequency that can produce
a full output swing without distortion caused by slew rate limiting is computed as
If we attempt to amplify frequencies higher than 6.12 kilohertz (and full amplitude)
with the circuit shown in Figure 2.3, then the output will be nonsinusoidal. Once
the input frequency goes higher than a certain frequency (about 9 kilohertz in this
case), then the output amplitude begins to drop in addition to the distorted shape.
Maximum Input Voltage Swing. We have computed the voltage gain of the
circuit, and we know the maximum output voltage swing. We, therefore, have
enough information to compute the largest input signal that can be applied with-
out driving the amplifier into saturation.
Calculations for the present case are shown below:
Since we are working with sinusoidal waveforms, we might choose to express this
value as peak or RMS as shown below:
For our present circuit, we have