Page 114 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 114
Light Sources and Transmitters
104 Chapter Six
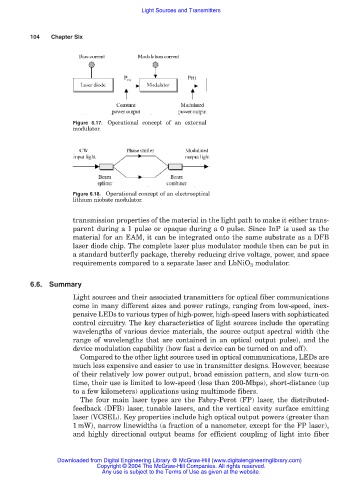
Figure 6.17. Operational concept of an external
modulator.
Figure 6.18. Operational concept of an electrooptical
lithium niobate modulator.
transmission properties of the material in the light path to make it either trans-
parent during a 1 pulse or opaque during a 0 pulse. Since InP is used as the
material for an EAM, it can be integrated onto the same substrate as a DFB
laser diode chip. The complete laser plus modulator module then can be put in
a standard butterfly package, thereby reducing drive voltage, power, and space
requirements compared to a separate laser and LbNiO 3 modulator.
6.6. Summary
Light sources and their associated transmitters for optical fiber communications
come in many different sizes and power ratings, ranging from low-speed, inex-
pensive LEDs to various types of high-power, high-speed lasers with sophisticated
control circuitry. The key characteristics of light sources include the operating
wavelengths of various device materials, the source output spectral width (the
range of wavelengths that are contained in an optical output pulse), and the
device modulation capability (how fast a device can be turned on and off).
Compared to the other light sources used in optical communications, LEDs are
much less expensive and easier to use in transmitter designs. However, because
of their relatively low power output, broad emission pattern, and slow turn-on
time, their use is limited to low-speed (less than 200-Mbps), short-distance (up
to a few kilometers) applications using multimode fibers.
The four main laser types are the Fabry-Perot (FP) laser, the distributed-
feedback (DFB) laser, tunable lasers, and the vertical cavity surface emitting
laser (VCSEL). Key properties include high optical output powers (greater than
1mW), narrow linewidths (a fraction of a nanometer, except for the FP laser),
and highly directional output beams for efficient coupling of light into fiber
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.