Page 180 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 180
Active Optical Components
170 Chapter Ten
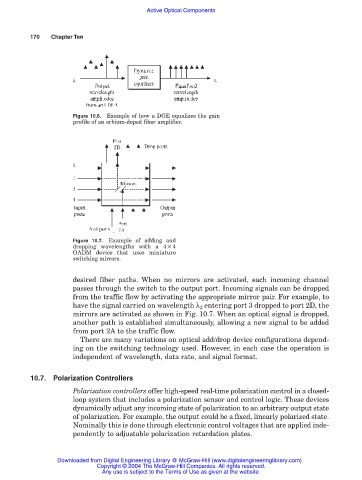
Figure 10.6. Example of how a DGE equalizes the gain
profile of an erbium-doped fiber amplifier.
Figure 10.7. Example of adding and
dropping wavelengths with a 4 4
OADM device that uses miniature
switching mirrors.
desired fiber paths. When no mirrors are activated, each incoming channel
passes through the switch to the output port. Incoming signals can be dropped
from the traffic flow by activating the appropriate mirror pair. For example, to
have the signal carried on wavelength λ 3 entering port 3 dropped to port 2D, the
mirrors are activated as shown in Fig. 10.7. When an optical signal is dropped,
another path is established simultaneously, allowing a new signal to be added
from port 2A to the traffic flow.
There are many variations on optical add/drop device configurations depend-
ing on the switching technology used. However, in each case the operation is
independent of wavelength, data rate, and signal format.
10.7. Polarization Controllers
Polarization controllers offer high-speed real-time polarization control in a closed-
loop system that includes a polarization sensor and control logic. These devices
dynamically adjust any incoming state of polarization to an arbitrary output state
of polarization. For example, the output could be a fixed, linearly polarized state.
Nominally this is done through electronic control voltages that are applied inde-
pendently to adjustable polarization retardation plates.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.