Page 231 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 231
Constructing the WDM Network Puzzle
Constructing the WDM Network Puzzle 221
13.2. Component Performance in WDM Links
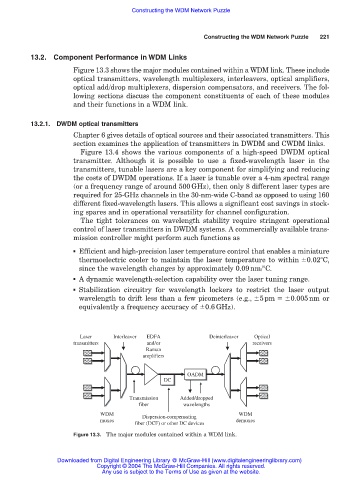
Figure 13.3 shows the major modules contained within a WDM link. These include
optical transmitters, wavelength multiplexers, interleavers, optical amplifiers,
optical add/drop multiplexers, dispersion compensators, and receivers. The fol-
lowing sections discuss the component constituents of each of these modules
and their functions in a WDM link.
13.2.1. DWDM optical transmitters
Chapter 6 gives details of optical sources and their associated transmitters. This
section examines the application of transmitters in DWDM and CWDM links.
Figure 13.4 shows the various components of a high-speed DWDM optical
transmitter. Although it is possible to use a fixed-wavelength laser in the
transmitters, tunable lasers are a key component for simplifying and reducing
the costs of DWDM operations. If a laser is tunable over a 4-nm spectral range
(or a frequency range of around 500GHz), then only 8 different laser types are
required for 25-GHz channels in the 30-nm-wide C-band as opposed to using 160
different fixed-wavelength lasers. This allows a significant cost savings in stock-
ing spares and in operational versatility for channel configuration.
The tight tolerances on wavelength stability require stringent operational
control of laser transmitters in DWDM systems. A commercially available trans-
mission controller might perform such functions as
■ Efficient and high-precision laser temperature control that enables a miniature
thermoelectric cooler to maintain the laser temperature to within 0.02°C,
since the wavelength changes by approximately 0.09nm/°C.
■ A dynamic wavelength-selection capability over the laser tuning range.
■ Stabilization circuitry for wavelength lockers to restrict the laser output
wavelength to drift less than a few picometers (e.g., 5pm 0.005nm or
equivalently a frequency accuracy of 0.6GHz).
Laser Interleaver EDFA Deinterleaver Optical
transmitters and/or receivers
Raman
amplifiers
OADM
OADM
DC
DC
Transmission Added/dropped
fiber wavelengths
WDM Dispersion-compensating WDM
muxes demuxes
fiber (DCF) or other DC devices
Figure 13.3. The major modules contained within a WDM link.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.