Page 236 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 236
Constructing the WDM Network Puzzle
226 Chapter Thirteen
Spectral band C-band Multi-λ Optical power
splitter EDFA VOAs monitors
Transmission
fiber DCF
DCF
DCF
DCF
Distributed
Distributed
Raman L-band Spectral band
Raman
pump lasers EDFA combiner
pump lasers
Control electronics
Control electronics
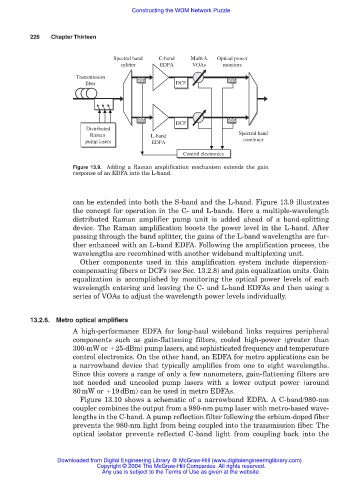
Figure 13.9. Adding a Raman amplification mechanism extends the gain
response of an EDFA into the L-band.
can be extended into both the S-band and the L-band. Figure 13.9 illustrates
the concept for operation in the C- and L-bands. Here a multiple-wavelength
distributed Raman amplifier pump unit is added ahead of a band-splitting
device. The Raman amplification boosts the power level in the L-band. After
passing through the band splitter, the gains of the L-band wavelengths are fur-
ther enhanced with an L-band EDFA. Following the amplification process, the
wavelengths are recombined with another wideband multiplexing unit.
Other components used in this amplification system include dispersion-
compensating fibers or DCFs (see Sec. 13.2.8) and gain equalization units. Gain
equalization is accomplished by monitoring the optical power levels of each
wavelength entering and leaving the C- and L-band EDFAs and then using a
series of VOAs to adjust the wavelength power levels individually.
13.2.6. Metro optical amplifiers
A high-performance EDFA for long-haul wideband links requires peripheral
components such as gain-flattening filters, cooled high-power (greater than
300-mW or 25-dBm) pump lasers, and sophisticated frequency and temperature
control electronics. On the other hand, an EDFA for metro applications can be
a narrowband device that typically amplifies from one to eight wavelengths.
Since this covers a range of only a few nanometers, gain-flattening filters are
not needed and uncooled pump lasers with a lower output power (around
80mW or 19dBm) can be used in metro EDFAs.
Figure 13.10 shows a schematic of a narrowband EDFA. A C-band/980-nm
coupler combines the output from a 980-nm pump laser with metro-based wave-
lengths in the C-band. A pump reflection filter following the erbium-doped fiber
prevents the 980-nm light from being coupled into the transmission fiber. The
optical isolator prevents reflected C-band light from coupling back into the
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.