Page 304 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 304
Optical Networks
294 Chapter Seventeen
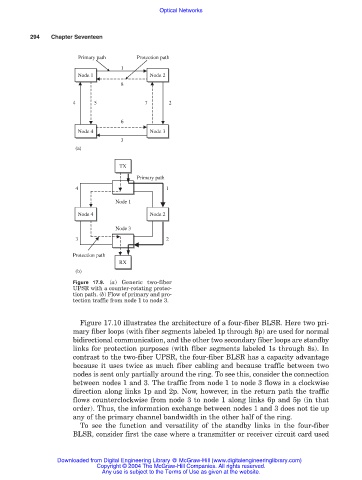
Primary path Protection path
1
Node 1 Node 2
Node 2
Node 1
8
4 5 7 2
6
Node 4 Node 3
Node 4
Node 3
3
(a)
TX
TX
Primary path
4 1
Node 1
Node 4 Node 2
Node 4
Node 2
Node 3
3 2
Protection path
RX
RX
(b)
Figure 17.9. (a) Generic two-fiber
UPSR with a counter-rotating protec-
tion path. (b) Flow of primary and pro-
tection traffic from node 1 to node 3.
Figure 17.10 illustrates the architecture of a four-fiber BLSR. Here two pri-
mary fiber loops (with fiber segments labeled 1p through 8p) are used for normal
bidirectional communication, and the other two secondary fiber loops are standby
links for protection purposes (with fiber segments labeled 1s through 8s). In
contrast to the two-fiber UPSR, the four-fiber BLSR has a capacity advantage
because it uses twice as much fiber cabling and because traffic between two
nodes is sent only partially around the ring. To see this, consider the connection
between nodes 1 and 3. The traffic from node 1 to node 3 flows in a clockwise
direction along links 1p and 2p. Now, however, in the return path the traffic
flows counterclockwise from node 3 to node 1 along links 6p and 5p (in that
order). Thus, the information exchange between nodes 1 and 3 does not tie up
any of the primary channel bandwidth in the other half of the ring.
To see the function and versatility of the standby links in the four-fiber
BLSR, consider first the case where a transmitter or receiver circuit card used
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.