Page 319 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 319
Network Management
Network Management 309
then can generate a bill or a tariff for the usage of the service as well as ensure
continued fair and optimal resource utilization.
18.2.4. Fault management
Faults in a network, such as physical cuts in a fiber transmission line or failure
of a circuit card or optical amplifier, can cause portions of a network to be inop-
erable. Since network faults can result in system downtime or unacceptable net-
work degradation, fault management is one of the most widely implemented
and important network management functions. With the growing dependence
of people on network resources for carrying out their work and communica-
tions, users expect rapid and reliable resolutions of network fault conditions. As
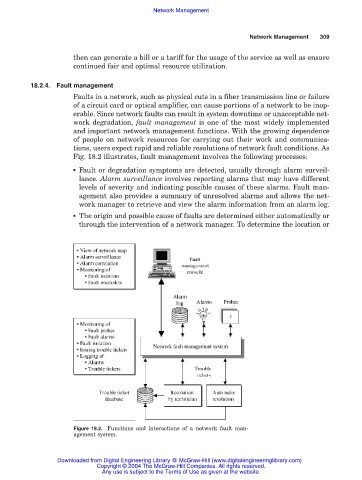
Fig. 18.2 illustrates, fault management involves the following processes:
■ Fault or degradation symptoms are detected, usually through alarm surveil-
lance. Alarm surveillance involves reporting alarms that may have different
levels of severity and indicating possible causes of these alarms. Fault man-
agement also provides a summary of unresolved alarms and allows the net-
work manager to retrieve and view the alarm information from an alarm log.
■ The origin and possible cause of faults are determined either automatically or
through the intervention of a network manager. To determine the location or
Figure 18.2. Functions and interactions of a network fault man-
agement system.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.