Page 317 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 317
Network Management
Network Management 307
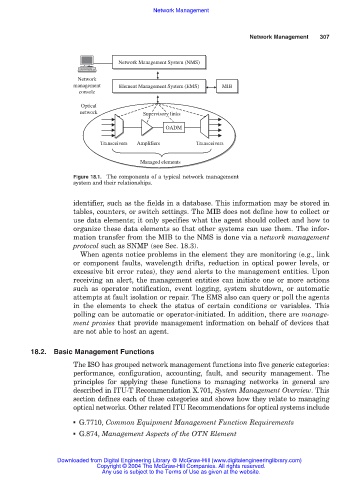
Network Management System (NMS)
Network Management System (NMS)
Network
management Element Management System (EMS) MIB
Element Management System (EMS)
MIB
console
Optical
network Supervisory links
OADM
Transceivers Amplifiers Transceivers
Managed elements
Figure 18.1. The components of a typical network management
system and their relationships.
identifier, such as the fields in a database. This information may be stored in
tables, counters, or switch settings. The MIB does not define how to collect or
use data elements; it only specifies what the agent should collect and how to
organize these data elements so that other systems can use them. The infor-
mation transfer from the MIB to the NMS is done via a network management
protocol such as SNMP (see Sec. 18.3).
When agents notice problems in the element they are monitoring (e.g., link
or component faults, wavelength drifts, reduction in optical power levels, or
excessive bit error rates), they send alerts to the management entities. Upon
receiving an alert, the management entities can initiate one or more actions
such as operator notification, event logging, system shutdown, or automatic
attempts at fault isolation or repair. The EMS also can query or poll the agents
in the elements to check the status of certain conditions or variables. This
polling can be automatic or operator-initiated. In addition, there are manage-
ment proxies that provide management information on behalf of devices that
are not able to host an agent.
18.2. Basic Management Functions
The ISO has grouped network management functions into five generic categories:
performance, configuration, accounting, fault, and security management. The
principles for applying these functions to managing networks in general are
described in ITU-T Recommendation X.701, System Management Overview. This
section defines each of these categories and shows how they relate to managing
optical networks. Other related ITU Recommendations for optical systems include
■ G.7710, Common Equipment Management Function Requirements
■ G.874, Management Aspects of the OTN Element
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.