Page 53 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 53
The Behavior of Light
The Behavior of Light 43
Figure 3.8. A Faraday rotator is a device that
rotates the state of polarization clockwise by
45° or one-quarter wavelength.
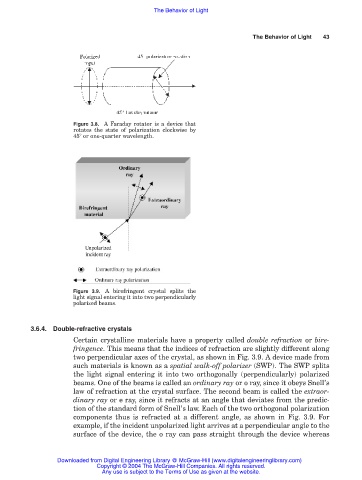
Figure 3.9. A birefringent crystal splits the
light signal entering it into two perpendicularly
polarized beams.
3.6.4. Double-refractive crystals
Certain crystalline materials have a property called double refraction or bire-
fringence. This means that the indices of refraction are slightly different along
two perpendicular axes of the crystal, as shown in Fig. 3.9. A device made from
such materials is known as a spatial walk-off polarizer (SWP). The SWP splits
the light signal entering it into two orthogonally (perpendicularly) polarized
beams. One of the beams is called an ordinary ray or o ray, since it obeys Snell’s
law of refraction at the crystal surface. The second beam is called the extraor-
dinary ray or e ray, since it refracts at an angle that deviates from the predic-
tion of the standard form of Snell’s law. Each of the two orthogonal polarization
components thus is refracted at a different angle, as shown in Fig. 3.9. For
example, if the incident unpolarized light arrives at a perpendicular angle to the
surface of the device, the o ray can pass straight through the device whereas
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.