Page 54 - Optical Switching And Networking Handbook
P. 54
03_200023_CH02/Batesx 1/17/01 8:17 AM Page 39
Basic Fiberoptics Technologies 39
sage of the light and the path used to get from one end to the other.
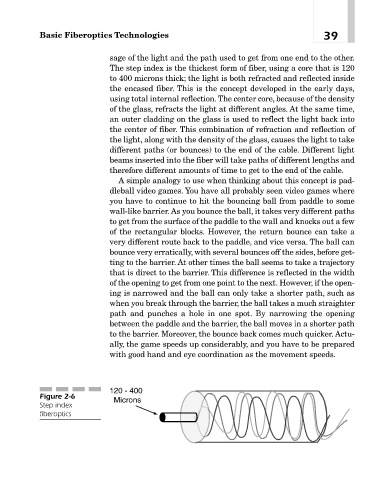
The step index is the thickest form of fiber, using a core that is 120
to 400 microns thick; the light is both refracted and reflected inside
the encased fiber. This is the concept developed in the early days,
using total internal reflection.The center core, because of the density
of the glass, refracts the light at different angles. At the same time,
an outer cladding on the glass is used to reflect the light back into
the center of fiber. This combination of refraction and reflection of
the light, along with the density of the glass, causes the light to take
different paths (or bounces) to the end of the cable. Different light
beams inserted into the fiber will take paths of different lengths and
therefore different amounts of time to get to the end of the cable.
A simple analogy to use when thinking about this concept is pad-
dleball video games. You have all probably seen video games where
you have to continue to hit the bouncing ball from paddle to some
wall-like barrier.As you bounce the ball, it takes very different paths
to get from the surface of the paddle to the wall and knocks out a few
of the rectangular blocks. However, the return bounce can take a
very different route back to the paddle, and vice versa. The ball can
bounce very erratically, with several bounces off the sides, before get-
ting to the barrier. At other times the ball seems to take a trajectory
that is direct to the barrier. This difference is reflected in the width
of the opening to get from one point to the next. However, if the open-
ing is narrowed and the ball can only take a shorter path, such as
when you break through the barrier, the ball takes a much straighter
path and punches a hole in one spot. By narrowing the opening
between the paddle and the barrier, the ball moves in a shorter path
to the barrier. Moreover, the bounce back comes much quicker. Actu-
ally, the game speeds up considerably, and you have to be prepared
with good hand and eye coordination as the movement speeds.
Figure 2-6
Step index
fiberoptics