Page 55 - Optical Switching And Networking Handbook
P. 55
03_200023_CH02/Batesx 1/17/01 8:17 AM Page 40
40 Chapter 2
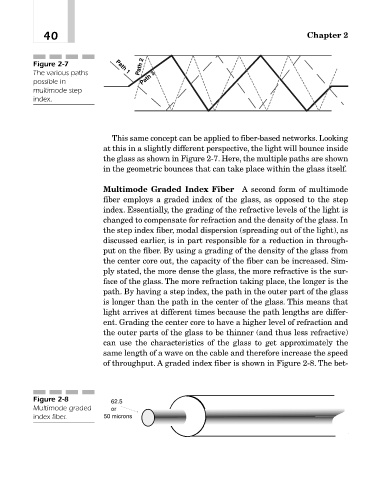
Figure 2-7 Path 1 Path 2
The various paths
possible in Path 3
multimode step
index.
This same concept can be applied to fiber-based networks. Looking
at this in a slightly different perspective, the light will bounce inside
the glass as shown in Figure 2-7. Here, the multiple paths are shown
in the geometric bounces that can take place within the glass itself.
Multimode Graded Index Fiber A second form of multimode
fiber employs a graded index of the glass, as opposed to the step
index. Essentially, the grading of the refractive levels of the light is
changed to compensate for refraction and the density of the glass. In
the step index fiber, modal dispersion (spreading out of the light), as
discussed earlier, is in part responsible for a reduction in through-
put on the fiber. By using a grading of the density of the glass from
the center core out, the capacity of the fiber can be increased. Sim-
ply stated, the more dense the glass, the more refractive is the sur-
face of the glass. The more refraction taking place, the longer is the
path. By having a step index, the path in the outer part of the glass
is longer than the path in the center of the glass. This means that
light arrives at different times because the path lengths are differ-
ent. Grading the center core to have a higher level of refraction and
the outer parts of the glass to be thinner (and thus less refractive)
can use the characteristics of the glass to get approximately the
same length of a wave on the cable and therefore increase the speed
of throughput. A graded index fiber is shown in Figure 2-8. The bet-
Figure 2-8 62.5
Multimode graded or
index fiber. 50 microns