Page 76 - Optical Switching And Networking Handbook
P. 76
04_200023_CH03/Batesx 1/17/01 9:42 AM Page 61
SONET 61
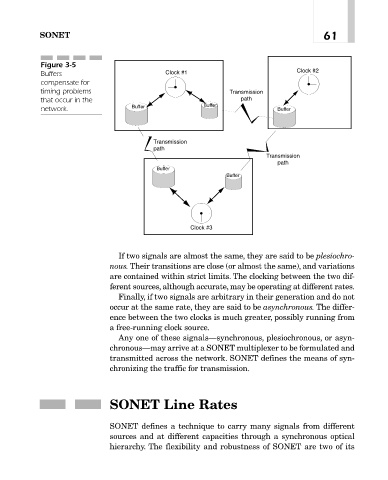
Figure 3-5
Buffers Clock #1 Clock #2
compensate for
timing problems Transmission
that occur in the path
network. Buffer Buffer Buffer
Transmission
path
Transmission
path
Buffer
Buffer
Clock #3
If two signals are almost the same, they are said to be plesiochro-
nous. Their transitions are close (or almost the same), and variations
are contained within strict limits. The clocking between the two dif-
ferent sources, although accurate, may be operating at different rates.
Finally, if two signals are arbitrary in their generation and do not
occur at the same rate, they are said to be asynchronous. The differ-
ence between the two clocks is much greater, possibly running from
a free-running clock source.
Any one of these signals—synchronous, plesiochronous, or asyn-
chronous—may arrive at a SONET multiplexer to be formulated and
transmitted across the network. SONET defines the means of syn-
chronizing the traffic for transmission.
SONET Line Rates
SONET defines a technique to carry many signals from different
sources and at different capacities through a synchronous optical
hierarchy. The flexibility and robustness of SONET are two of its