Page 250 - Optofluidics Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications
P. 250
Bio-Inspir ed Fluidic Lenses for Imaging and Integrated Optics 225
visual acuity needed to discriminate two points separated by 1 arc
minute and considered to be normal vision. Figure 9-20 shows fruits
and green beans at 3.8 m and 45 cm, respectively. The results demon-
strate a 4-D tuning range of fluidic IOL.
9-3-3 Mechanical Modeling of Fluidic Intraocular Lens
Movement of the ciliary muscle from contracted/accommodated state
to the relaxed/unaccommodated state increases tension in the zonules
and changes the capsular bag into a thinner and longer shape. The
state-of-art technique to actuate the IOL is by utilizing the shape change
of the capsular bag when the human eye accommodates. In order to
explore the pressure distribution of fluidic IOL, the mechanism of
membrane is simulated using finite element analysis. A nonlinear
hyperelastic model is applied to the PDMS membrane. Assuming the
fluidic IOL is rotational symmetric, one can simplify the computation
using an axisymmetric model [70]. The simulated IOL profile under
given fluidic pressure is then fitted to an elliptical equation [Eq. (9-1)]
characterized by the radius of curvature and conic factor [71]. The conic
factor accounts for any aspherical profile of the fluidic IOL to the first
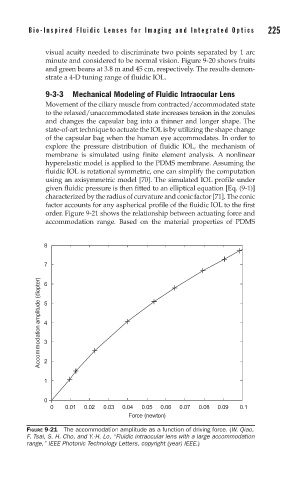
order. Figure 9-21 shows the relationship between actuating force and
accommodation range. Based on the material properties of PDMS
8
7 6
Accommodation amplitude (diopter) 5 5 4 3
1 2
0
0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.1
Force (newton)
FIGURE 9-21 The accommodation amplitude as a function of driving force. (W. Qiao,
F. Tsai, S. H. Cho, and Y.-H. Lo, “Fluidic intraocular lens with a large accommodation
range,” IEEE Photonic Technology Letters, copyright (year) IEEE.)