Page 174 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 174
148 PVT Property Correlations
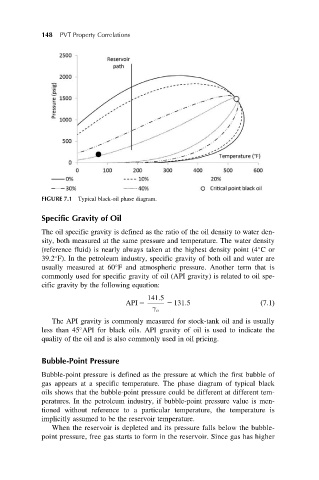
FIGURE 7.1 Typical black-oil phase diagram.
Specific Gravity of Oil
The oil specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the oil density to water den-
sity, both measured at the same pressure and temperature. The water density
(reference fluid) is nearly always taken at the highest density point (4 Cor
39.2 F). In the petroleum industry, specific gravity of both oil and water are
usually measured at 60 F and atmospheric pressure. Another term that is
commonly used for specific gravity of oil (API gravity) is related to oil spe-
cific gravity by the following equation:
141:5
API 5 2 131:5 ð7:1Þ
γ o
The API gravity is commonly measured for stock-tank oil and is usually
less than 45 API for black oils. API gravity of oil is used to indicate the
quality of the oil and is also commonly used in oil pricing.
Bubble-Point Pressure
Bubble-point pressure is defined as the pressure at which the first bubble of
gas appears at a specific temperature. The phase diagram of typical black
oils shows that the bubble-point pressure could be different at different tem-
peratures. In the petroleum industry, if bubble-point pressure value is men-
tioned without reference to a particular temperature, the temperature is
implicitly assumed to be the reservoir temperature.
When the reservoir is depleted and its pressure falls below the bubble-
point pressure, free gas starts to form in the reservoir. Since gas has higher