Page 179 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 179
Black Oils Chapter | 7 153
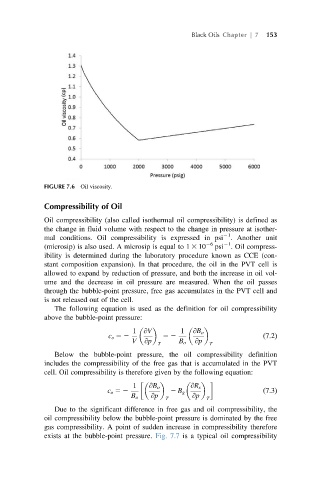
FIGURE 7.6 Oil viscosity.
Compressibility of Oil
Oil compressibility (also called isothermal oil compressibility) is defined as
the change in fluid volume with respect to the change in pressure at isother-
21
mal conditions. Oil compressibility is expressed in psi . Another unit
21
(microsip) is also used. A microsip is equal to 1 3 10 26 psi . Oil compress-
ibility is determined during the laboratory procedure known as CCE (con-
stant composition expansion). In that procedure, the oil in the PVT cell is
allowed to expand by reduction of pressure, and both the increase in oil vol-
ume and the decrease in oil pressure are measured. When the oil passes
through the bubble-point pressure, free gas accumulates in the PVT cell and
is not released out of the cell.
The following equation is used as the definition for oil compressibility
above the bubble-point pressure:
1 @V 1 @B o
c o 52 52 ð7:2Þ
V @p @p
T B o T
Below the bubble-point pressure, the oil compressibility definition
includes the compressibility of the free gas that is accumulated in the PVT
cell. Oil compressibility is therefore given by the following equation:
1 @B o @R s
c o 52 2 B g ð7:3Þ
B o @p @p
T T
Due to the significant difference in free gas and oil compressibility, the
oil compressibility below the bubble-point pressure is dominated by the free
gas compressibility. A point of sudden increase in compressibility therefore
exists at the bubble-point pressure. Fig. 7.7 is a typical oil compressibility