Page 22 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 22
Introduction Chapter | 1 3
variation in MBO properties, leading to errors in recovery predictions from
the simulator.
It is generally observed that estimation of correct PVT properties is more
challenging for more volatile fluids. Reserves and production calculations
are the most sensitive to errors in PVT data for more volatile fluids.
SATURATED AND UNDERSATURATED RESERVOIRS
Undersaturated reservoirs or fluids are reservoirs whose initial pressure is
above the saturation pressure of the fluid. The saturation pressure is called
bubble point pressure for oils, and dew point pressure for gases. The majority
of oil and gas reservoirs are discovered in the undersaturated state. The reser-
voir or the fluid it contains is said to be “saturated” if the initial reservoir
pressure is the same as the saturation pressure.
When a reservoir is discovered as a saturated reservoir, two phases coex-
ist: hydrocarbon liquid or oil phase, and hydrocarbon vapor or gas phase.
The two phases are separated by a gas oil contact (GOC). If the main fluid
in the reservoir is oil, the reservoir is called “gas cap oil reservoir.” If the
dominant fluid is gas condensate, the oil zone is usually termed “oil rim.”
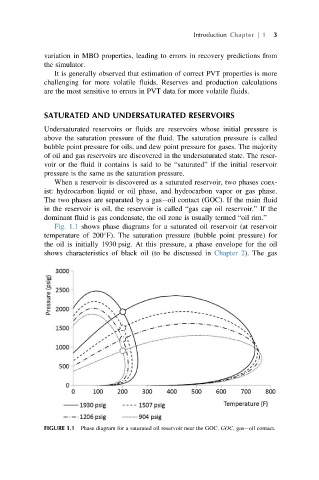
Fig. 1.1 shows phase diagrams for a saturated oil reservoir (at reservoir
temperature of 200 F). The saturation pressure (bubble point pressure) for
the oil is initially 1930 psig. At this pressure, a phase envelope for the oil
shows characteristics of black oil (to be discussed in Chapter 2). The gas
FIGURE 1.1 Phase diagram for a saturated oil reservoir near the GOC. GOC, gas oil contact.