Page 257 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 257
226 PVT Property Correlations
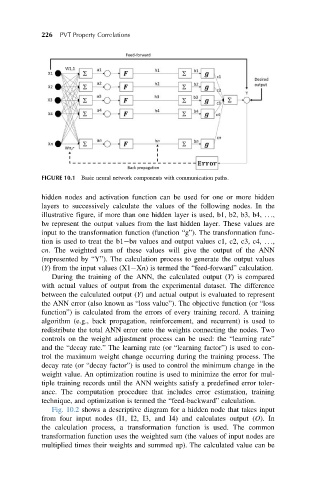
FIGURE 10.1 Basic neural network components with communication paths.
hidden nodes and activation function can be used for one or more hidden
layers to successively calculate the values of the following nodes. In the
illustrative figure, if more than one hidden layer is used, b1, b2, b3, b4, ...,
bn represent the output values from the last hidden layer. These values are
input to the transformation function (function “g”). The transformation func-
tion is used to treat the b1 bn values and output values c1, c2, c3, c4, ...,
cn. The weighted sum of these values will give the output of the ANN
(represented by “Y”). The calculation process to generate the output values
(Y) from the input values (X1 Xn) is termed the “feed-forward” calculation.
During the training of the ANN, the calculated output (Y) is compared
with actual values of output from the experimental dataset. The difference
between the calculated output (Y) and actual output is evaluated to represent
the ANN error (also known as “loss value”). The objective function (or “loss
function”) is calculated from the errors of every training record. A training
algorithm (e.g., back propagation, reinforcement, and recurrent) is used to
redistribute the total ANN error onto the weights connecting the nodes. Two
controls on the weight adjustment process can be used: the “learning rate”
and the “decay rate.” The learning rate (or “learning factor”) is used to con-
trol the maximum weight change occurring during the training process. The
decay rate (or “decay factor”) is used to control the minimum change in the
weight value. An optimization routine is used to minimize the error for mul-
tiple training records until the ANN weights satisfy a predefined error toler-
ance. The computation procedure that includes error estimation, training
technique, and optimization is termed the “feed-backward” calculation.
Fig. 10.2 shows a descriptive diagram for a hidden node that takes input
from four input nodes (I1, I2, I3, and I4) and calculates output (O). In
the calculation process, a transformation function is used. The common
transformation function uses the weighted sum (the values of input nodes are
multiplied times their weights and summed up). The calculated value can be